Qualitative and quantitative analyses of impact of COVID-19 on sustainable development goals (SDGs) in Indian subcontinent with a focus on air quality
- PMID: 33552191
- PMCID: PMC7846907
- DOI: 10.1007/s13762-020-03122-z
Qualitative and quantitative analyses of impact of COVID-19 on sustainable development goals (SDGs) in Indian subcontinent with a focus on air quality
Abstract
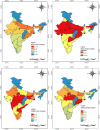
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is spreading all over the world in a short time. It originated from Wuhan City of China in the late 2019. Proper vaccines have still been in progress; the spread of the virus is contracted by lockdown and social distancing protocols. These lockdowns resulted in significant benefits, improving the quality of air and reducing the level of environmental pollution. In this context, the study proposes to identify the air quality in the region and its relation with COVID-19-affected people in metropolitan cities of India during COVID-19 lockdowns using a geographical information system (GIS), where over 90% of commercial and industrial sites and 100% school and colleges were closed. The study outcomes highlight the areas encountering high levels of pollution under the pre-lockdown scenario and have seen a higher number of cases. The relation is most evident for PM2.5, which is responsible for respiratory disorders and is the place of attack of SARS-CoV-2. This approach provides comparable outcomes with other decision-making tools. Our primary precedence should be to develop communities to enable people to remain healthy and stay. Healthy societies are crucial not only for people's health, but also for sustainable development. Centered on GIS is concealed; moreover, it is very flexible to use by policymakers.
Keywords: COVID-19; Coronavirus; Fine particulate matter; GIS; Ozone (O3); SDGs; Thiessen polygon.
© Islamic Azad University (IAU) 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Assessment of air pollution status during COVID-19 lockdown (March-May 2020) over Bangalore City in India.Environ Monit Assess. 2021 Jun 8;193(7):395. doi: 10.1007/s10661-021-09177-w. Environ Monit Assess. 2021. PMID: 34105059 Free PMC article.
-
Environmental impacts of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19).Bioresour Technol Rep. 2021 Sep;15:100744. doi: 10.1016/j.biteb.2021.100744. Epub 2021 Jun 25. Bioresour Technol Rep. 2021. PMID: 34189443 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Unprecedented reduction in air pollution and corresponding short-term premature mortality associated with COVID-19 lockdown in Delhi, India.J Air Waste Manag Assoc. 2021 Sep;71(9):1085-1101. doi: 10.1080/10962247.2021.1905104. Epub 2021 Apr 15. J Air Waste Manag Assoc. 2021. PMID: 33764280
-
Amplified ozone pollution in cities during the COVID-19 lockdown.Sci Total Environ. 2020 Sep 15;735:139542. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139542. Epub 2020 May 20. Sci Total Environ. 2020. PMID: 32447070 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 lockdown and environmental pollution: an Indian multi-state investigation.Environ Monit Assess. 2022 Jan 3;194(2):49. doi: 10.1007/s10661-021-09693-9. Environ Monit Assess. 2022. PMID: 34978634 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Is safe distance enough to prevent COVID-19? Dispersion and tracking of aerosols in various artificial ventilation conditions using OpenFOAM.Gondwana Res. 2023 Feb;114:40-54. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2022.03.013. Epub 2022 Apr 8. Gondwana Res. 2023. PMID: 35431597 Free PMC article.
-
Toward Environmental Sustainability, Health, and Equity: How the Psychological Characteristics of College Students Are Reflected in Understanding Sustainable Development Goals.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Aug 3;18(15):8217. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18158217. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 34360510 Free PMC article.
-
Recovery agenda for sustainable development post COVID-19 at the country level: developing a fuzzy action priority surface.Environ Dev Sustain. 2021;23(11):16646-16673. doi: 10.1007/s10668-021-01372-6. Epub 2021 Apr 3. Environ Dev Sustain. 2021. PMID: 33841039 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment and valuation of health impacts of fine particulate matter during COVID-19 lockdown: a comprehensive study of tropical and sub tropical countries.Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021 Aug;28(32):44522-44537. doi: 10.1007/s11356-021-13813-w. Epub 2021 Apr 14. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int. 2021. PMID: 33852112 Free PMC article.
-
COVID-19 and Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs): Scenario analysis through fuzzy cognitive map modeling.Gondwana Res. 2023 Feb;114:138-155. doi: 10.1016/j.gr.2021.12.014. Epub 2022 Jan 29. Gondwana Res. 2023. PMID: 35132304 Free PMC article.
References
-
- AajTak news (2020) Retrieved from May 31, 2020. https://aajtak.intoday.in/
-
- Bhalekar V. Novel corona virus pandemic-impact on Indian economy. E-Commer Educ Employ. 2020 doi: 10.2139/ssrn.3580342. - DOI
-
- Bharadwaj S, Singh S, Singh A, Singh HK, Singh HK et al (2020) Preprints, Basel, May 24. https://doi.org/10.20944/preprints202005.0403.v1
-
- Bhat BA, Gull S, Jeelani G, et al. A Study on COVID-19 lockdown impact on food, agriculture, fisheries and precautionary measures to avoid COVID-19 contamination. Galore Int J Appl Sci Human. 2020;4(2):8–18.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
