High throughput sequencing reveals the abundance and diversity of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in aquaculture wastewaters, Shandong, China
- PMID: 33552832
- PMCID: PMC7847479
- DOI: 10.1007/s13205-021-02656-4
High throughput sequencing reveals the abundance and diversity of antibiotic-resistant bacteria in aquaculture wastewaters, Shandong, China
Abstract
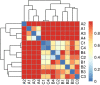
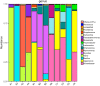
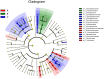
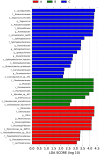
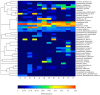
An innovative investigation was undertaken into the abundance and diversity of high antibiotic-resistant bacteria in aquaculture waters in Shandong Province, China, through cumulation incubation, PCR amplification of 16S rDNA, and high-throughput sequencing. The results showed that Vibrio, Bacillus, Vagococcus, Acinetobacter, Shewanella, Psychrobacter, Lactococcus, Enterococcus, Marinimonus and Myroids were abundant in the aquaculture waters, whereas other phylum including Actinobacteria, Deinococcus-Thermus, Omnitrophica and Nitrospirae had relatively lower abundance. Our studies revealed the presence of different bacteria in different locations in the aquaculture waters, most of which were resistant to multiple antibiotics. That is, the same microbial species from the same aquaculture wastewater can resist different antibiotics. Altogether, a considerable portion of the microbial community were found to be multi-drug resistant. It is essential that the spread of the antibiotic-resistant bacteria is controlled so that the distribution of antibiotic resistance genes to other environments is avoided.
Supplementary information: The online version contains supplementary material available at 10.1007/s13205-021-02656-4.
Keywords: Antibiotic-resistant bacteria; Aquaculture waters; High-throughput sequencing; Multi-drug resistant.
© King Abdulaziz City for Science and Technology 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestNo conflict of interest was declared in the publication.
Figures


References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

