Extracellular Vesicles in Musculoskeletal Pathologies and Regeneration
- PMID: 33553127
- PMCID: PMC7855463
- DOI: 10.3389/fbioe.2020.624096
Extracellular Vesicles in Musculoskeletal Pathologies and Regeneration
Abstract
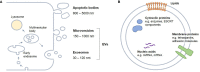
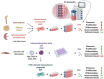
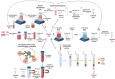
The incidence of musculoskeletal diseases is steadily increasing with aging of the population. In the past years, extracellular vesicles (EVs) have gained attention in musculoskeletal research. EVs have been associated with various musculoskeletal pathologies as well as suggested as treatment option. EVs play a pivotal role in communication between cells and their environment. Thereby, the EV cargo is highly dependent on their cellular origin. In this review, we summarize putative mechanisms by which EVs can contribute to musculoskeletal tissue homeostasis, regeneration and disease, in particular matrix remodeling and mineralization, pro-angiogenic effects and immunomodulatory activities. Mesenchymal stromal cells (MSCs) present the most frequently used cell source for EV generation for musculoskeletal applications, and herein we discuss how the MSC phenotype can influence the cargo and thus the regenerative potential of EVs. Induced pluripotent stem cell-derived mesenchymal progenitor cells (iMPs) may overcome current limitations of MSCs, and iMP-derived EVs are discussed as an alternative strategy. In the last part of the article, we focus on therapeutic applications of EVs and discuss both practical considerations for EV production and the current state of EV-based therapies.
Keywords: MSC; cell-free therapeutics; exosomes; extracellular vesicles; iMP; musculoskeletal diseases.
Copyright © 2021 Herrmann, Diederichs, Melnik, Riegger, Trivanović, Li, Jenei-Lanzl, Brenner, Huber-Lang, Zaucke, Schildberg and Grässel.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Abbas M., Jesel L., Auger C., Amoura L., Messas N., Manin G., et al. . (2017). Endothelial microparticles from acute coronary syndrome patients induce premature coronary artery endothelial cell aging and thrombogenicity: role of the Ang II/AT1 receptor/NADPH oxidase-mediated activation of MAPKs and PI3-kinase pathways. Circulation 135, 280–296. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.017513 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Ahn S. Y., Park W. S., Kim Y. E., Sung D. K., Sung S. I., Ahn J. Y., et al. . (2018). Vascular endothelial growth factor mediates the therapeutic efficacy of mesenchymal stem cell-derived extracellular vesicles against neonatal hyperoxic lung injury. Exp. Mol. Med. 50:26. 10.1038/s12276-018-0055-8 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

