Diagnosis value of SARS-CoV-2 antigen/antibody combined testing using rapid diagnostic tests at hospital admission
- PMID: 33554363
- PMCID: PMC8013599
- DOI: 10.1002/jmv.26855
Diagnosis value of SARS-CoV-2 antigen/antibody combined testing using rapid diagnostic tests at hospital admission
Abstract
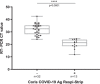
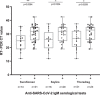
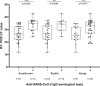
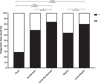
The implementation of rapid diagnostic tests (RDTs) may enhance the efficiency of severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) testing, as RDTs are widely accessible and easy to use. The aim of this study was to evaluate the performance of a diagnosis strategy based on a combination of antigen and immunoglobulin M (IgM) or immunoglobulin G (IgG) serological RDTs. Plasma and nasopharyngeal samples were collected between 14 March and 11 April 2020 at hospital admission from 45 patients with reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR) confirmed COVID-19 and 20 negative controls. SARS-CoV-2 antigen (Ag) was assessed in nasopharyngeal swabs using the Coris Respi-Strip. For IgM/IgG detection, SureScreen Diagnostics and Szybio Biotech RDTs were used in addition to laboratory assays (Abbott Alinity i SARS-CoV-2 IgG and Theradiag COVID-19 IgM enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay). Using the Ag RDT, 13 out of 45 (29.0%) specimens tested positive, the sensitivity was 87.0% for cycle threshold (Ct ) values ≤25% and 0% for Ct values greater than 25. IgG detection was associated with high Ct values and the amount of time after the onset of symptoms. The profile of isolated IgM on RDTs was more frequently observed during the first and second week after the onset of symptoms. The combination of Ag and IgM/IgG RDTs enabled the detection of up to 84.0% of COVID-19 confirmed cases at hospital admission. Antigen and antibody-based RDTs showed suboptimal performances when used alone. However when used in combination, they are able to identify most COVID-19 patients admitted in an emergency department.
Keywords: SARS-CoV-2 antibody; SARS-CoV-2 antigen; coronavirus disease-19 (COVID-19); diagnosis; rapid diagnostic tests.
© 2021 Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no conflict of interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

