Epidemics and trust: The case of the Spanish Flu
- PMID: 33554412
- PMCID: PMC7986373
- DOI: 10.1002/hec.4218
Epidemics and trust: The case of the Spanish Flu
Abstract
Recent studies argue that major crises can have long-lasting effects on individual behavior. While most studies focused on natural disasters, we explore the consequences of the global pandemic caused by a lethal influenza virus in 1918-19: the so-called "Spanish Flu." This was by far the worst pandemic of modern history, causing up to 100 million deaths worldwide. Using information about attitudes of respondents to the General Social Survey, we find evidence that experiencing the pandemic likely had permanent consequences in terms of individuals' social trust. Our findings suggest that lower social trust was passed on to the descendants of the survivors of the Spanish Flu who migrated to the United States. As trust is a crucial factor for long-term economic development, our research offers a new angle from which to assess current health threats.
Keywords: Spanish flu; epidemic; generalized trust; mortality crisis; pandemic.
© 2021 The Authors. Health Economics published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
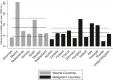
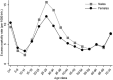
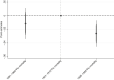
Figures
References
-
- Alfani, G. (2020). Pandemics and asymmetric shocks: Evidence from the history of plague in europe and the mediterranean. Technical report, CAGE Working Paper No. 478.
-
- Alfani, G. , & Murphy, T. (2017). Plague and lethal epidemics in the pre‐industrial world. Journal of Economic History, 77(1), 314–343.
-
- Alfani, G. , & Percoco, M. (2019). Plague and long‐term development: The lasting effects of the 1629–30 epidemic on the Italian cities. Economic History Review, 72(4), 1175–1201.
-
- Algan Y., & Cahuc P. (2010). Inherited Trust and Growth. American Economic Review, 100(5), 2060–2092. http://org/10.1257/aer.100.5.2060 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

