Mesenchymal stem cells protect renal tubular cells via TSG-6 regulating macrophage function and phenotype switching
- PMID: 33554782
- PMCID: PMC7988807
- DOI: 10.1152/ajprenal.00426.2020
Mesenchymal stem cells protect renal tubular cells via TSG-6 regulating macrophage function and phenotype switching
Abstract
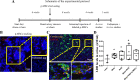
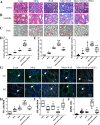
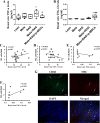
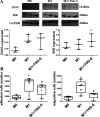
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α-induced gene/protein (TSG)-6 regulates the immunomodulatory properties of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs), but its ability to protect the ischemic kidney is unknown. In a swine model of renal artery stenosis (RAS) and metabolic syndrome (MetS), we assessed the contribution of TSG-6 produced by MSCs to their immunomodulatory properties. Pigs were studied after 16 wk of diet-induced MetS and unilateral RAS and were either untreated or treated 4 wk earlier with intrarenal autologous adipose tissue-derived MSCs (n = 6 each). Lean, MetS, and RAS sham animals served as controls. We studied renal function in vivo (using computed tomography) and kidney histopathology and macrophage phenotype ex vivo. In vitro, TSG-6 levels were also measured in conditioned media of human MSCs incubated with TNF-α and levels of the tubular injury marker lactate dehydrogenase in conditioned media after coculturing macrophages with injured human kidney 2 (HK-2) cells with or without TSG-6. The effects of TSG-6 on macrophage phenotype (M1/M2), adhesion, and migration were also determined. MetS + RAS showed increased M1 macrophages and renal vein TNF-α levels. After MSC delivery, renal vein TSG-6 increased and TNF-α decreased, the M1-to-M2 ratio decreased, renal function improved, and fibrosis was alleviated. In vitro, TNF-α increased TSG-6 secretion by human MSCs. TSG-6 decreased lactate dehydrogenase release from injured HK-2 cells, increased expression of macrophage M2 markers, and reduced M1 macrophage adhesion and migration. Therefore, TSG-6 released from MSCs may decrease renal tubular cell injury, which is associated with regulating macrophage function and phenotype. These observations suggest that TSG-6 is endowed with renoprotective properties.NEW & NOTEWORTHY Tumor necrosis factor-α-induced gene/protein (TSG)-6 regulates the immunomodulatory properties of MSCs, but its ability to protect the ischemic kidney is unknown. In pigs with renal artery stenosis, we show that MSC delivery increased renal vein TSG-6, decreased kidney inflammatory macrophages, and improved renal function. In vitro, TSG-6 decreased inflammatory macrophages and tubular cell injury. Therefore, TSG-6 released from MSCs may decrease renal tubular cell injury, which is associated with regulating macrophage function and phenotype.
Keywords: macrophage; mesenchymal stem cells; metabolic syndrome; renal artery stenosis; tumor necrosis factor-α-induced gene/protein-6.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 DK122734/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK104273/HHS | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK)
- U01 DK104273/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK120292/HHS | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK)
- R21 AG062104/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK120292/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK102325/HHS | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK)
- AG062104/HHS | NIH | National Institute on Aging (NIA)
- R01 DK102325/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK122734/HHS | NIH | National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases (NIDDK)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

