The C3/465 glycan hole cluster in BG505 HIV-1 envelope is the major neutralizing target involved in preventing mucosal SHIV infection
- PMID: 33556148
- PMCID: PMC7895394
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.ppat.1009257
The C3/465 glycan hole cluster in BG505 HIV-1 envelope is the major neutralizing target involved in preventing mucosal SHIV infection
Abstract
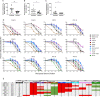
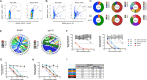
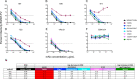
Stabilized HIV-1 envelope (Env) trimers elicit tier 2 autologous neutralizing antibody (nAb) responses in immunized animals. We previously demonstrated that BG505 SOSIP.664.T332N gp140 (BG505 SOSIP) immunization of rhesus macaques (RM) provided robust protection against autologous intra-vaginal simian-human immunodeficiency virus (SHIV) challenge that was predicted by high serum nAb titers. Here, we show that nAb in these protected RM targeted a glycan hole proximal to residue 465 in gp120 in all cases. nAb also targeted another glycan hole at residues 241/289 and an epitope in V1 at varying frequencies. Non-neutralizing antibodies directed at N611-shielded epitopes in gp41 were also present but were more prevalent in RM with low nAb titers. Longitudinal analysis demonstrated that nAb broadened in some RM during sequential immunization but remained focused in others, the latter being associated with increases in nAb titer. Thirty-eight monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) isolated from a protected RM with an exceptionally high serum neutralization titer bound to the trimer in ELISA, and four of the mAbs potently neutralized the BG505 Env pseudovirus (PV) and SHIV. The four neutralizing mAbs were clonally related and targeted the 465 glycan hole to varying degrees, mimicking the serum. The data demonstrate that the C3/465 glycan hole cluster was the dominant neutralization target in high titer protected RM, despite other co-circulating neutralizing and non-neutralizing specificities. The isolation of a neutralizing mAb family argues that clonotype expansion occurred during BG505 SOSIP immunization, leading to high titer, protective nAb and setting a desirable benchmark for HIV vaccines.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- Sanders RW, Derking R, Cupo A, Julien JP, Yasmeen A, de Val N, et al. A next-generation cleaved, soluble HIV-1 Env trimer, BG505 SOSIP.664 gp140, expresses multiple epitopes for broadly neutralizing but not non-neutralizing antibodies. PLoS Pathog. 2013;9(9):e1003618 10.1371/journal.ppat.1003618 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P51 OD011132/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- R61 AI161818/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI058706/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R21 AI150292/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI165080/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- U42 OD011023/OD/NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI169662/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI124436/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P30 AI050409/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- UM1 AI144462/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI160607/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AI128837/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- P01 AI131251/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
- F31 AI131873/AI/NIAID NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

