Asthma and risk of infection, hospitalization, ICU admission and mortality from COVID-19: Systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 33556287
- PMCID: PMC8022341
- DOI: 10.1080/02770903.2021.1888116
Asthma and risk of infection, hospitalization, ICU admission and mortality from COVID-19: Systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Objective: As COVID-19 spreads across the world, there are concerns that people with asthma are at a higher risk of acquiring the disease, or of poorer outcomes. This systematic review aimed to summarize evidence on the risk of infection, severe illness and death from COVID-19 in people with asthma.
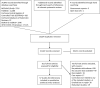
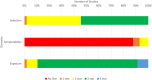
Data sources and study selection: A comprehensive search of electronic databases including preprint repositories and WHO COVID-19 database was conducted (until 26 May 2020). Studies reporting COVID-19 in people with asthma were included. For binary outcomes, we performed Sidik-Jonkman random effects meta-analysis. We explored quantitative heterogeneity by subgroup analyses, meta regression and evaluating the I2 statistic.
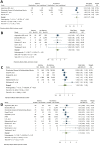
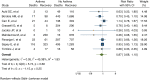
Results: Fifty-seven studies with an overall sample size of 587 280 were included. The prevalence of asthma among those infected with COVID-19 was 7.46% (95% CI = 6.25-8.67). Non-severe asthma was more common than severe asthma (9.61% vs. 4.13%). Pooled analysis showed a 14% risk ratio reduction in acquiring COVID-19 (95% CI = 0.80-0.94; p < 0.0001) and 13% reduction in hospitalization with COVID-19 (95% CI = 0.77-0.99, p = 0.03) for people with asthma compared with those without. There was no significant difference in the combined risk of requiring admission to ICU and/or receiving mechanical ventilation for people with asthma (RR = 0.87 95% CI = 0.94-1.37; p = 0.19) and risk of death from COVID-19 (RR = 0.87; 95% CI = 0.68-1.10; p = 0.25).
Conclusion: The findings from this study suggest that the prevalence of people with asthma among COVID-19 patients is similar to the global prevalence of asthma. The overall findings suggest that people with asthma have a lower risk than those without asthma for acquiring COVID-19 and have similar clinical outcomes.
Keywords: Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2; coronavirus; critical care medicine; meta-analysis; novel coronavirus 2019; respiratory infections; ventilator support.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no conflict of interest. AS is in receipt of a UNSW Scientia PhD scholarship.
Figures

References
-
- US CDC . COVID-NET Preliminary Data 30 May 2020. Available from: https://gis.cdc.gov/grasp/COVIDNet/COVID19_5.html [last accessed 6 June 2020].
-
- NICE UK . COVID-19 rapid guideline: Severe asthma; 2020. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials
