Alpha emitting nuclides for targeted therapy
- PMID: 33558017
- PMCID: PMC8363053
- DOI: 10.1016/j.nucmedbio.2020.08.004
Alpha emitting nuclides for targeted therapy
Abstract
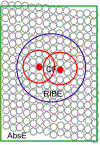
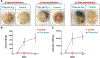
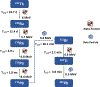
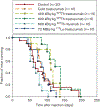
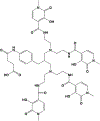
Targeted alpha therapy (TAT) is an area of research with rapidly increasing importance as the emitted alpha particle has a significant effect on inducing cytotoxic effects on tumor cells while mitigating dose to normal tissues. Two significant isotopes of interest within the area of TAT are thorium-227 and actinium-225 due to their nuclear characteristics. Both isotopes have physical half-lives suitable for coordination with larger biomolecules, and additionally actinium-225 has potential to serve as an in vivo generator. In this review, the authors will discuss the production, purification, labeling reactions, and biological studies of actinium-225 and thorium-227 complexes and clinical studies.
Keywords: Actinium-225; Alpha therapy; Radiolabeling; Thorium-227.
Copyright © 2020. Published by Elsevier Inc.
Figures


References
-
- Sgouros G; Ballangrud AM; Jurcic JG; McDevitt MR; Humm JL; Erdi YE; Mehta BM; Finn RD; Larson SM; Scheinberg DA, Pharmacokinetics and dosimetry of an a-paticle emitter antibody: 213Bi-HuM195 (anti-CD33) in patients with leukemia. J. Nucl. Mater 1999, 40, 1935–1946. - PubMed
-
- Poty S; McDevitt Michael R; Lewis Jason S; Francesconi Lynn C; Francesconi Lynn C; McDevitt Michael R; Morris Michael J; Lewis Jason S, α-Emitters for Radiotherapy: From Basic Radiochemistry to Clinical Studies-Part 2. Journal of nuclear medicine : official publication, Society of Nuclear Medicine 2018, 59 (7), 1020–1027. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

