Kinetics and prognostic value of soluble VCAM-1 in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction patients
- PMID: 33559404
- PMCID: PMC8127550
- DOI: 10.1002/iid3.409
Kinetics and prognostic value of soluble VCAM-1 in ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction patients
Abstract
Background: Soluble vascular cell adhesion molecule-1 (sVCAM-1) is a biomarker of endothelial activation and inflammation. There is still controversy as to whether it can predict clinical outcome after ST-elevation myocardial infarction (STEMI). Our aim was to assess the sVCAM-1 kinetics and to evaluate its prognostic predictive value.
Method: We prospectively enrolled 251 consecutive STEMI patients who underwent coronary revascularization in our university hospital. Blood samples were collected at admission, 4, 24, 48 h and 1 month after admission. sVCAM-1 serum level was assessed using ELISA assay. All patients had cardiac magnetic resonance imaging at 1-month for infarct size (IS) and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) assessment. Clinical outcomes were recorded over 12 months after STEMI.
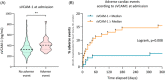
Results: sVCAM-1 levels significantly increased from admission up to 1 month and were significantly correlated with IS, LVEF, and LV end-systolic and diastolic volume. (H48 area under curve (AUC) ≥ H48 median) were associated with an increased risk of adverse clinical events during the 12-month follow-up period with a hazard ratio (HR) = 2.6 (95% confidence interval [CI] of ratio = 1.2-5.6, p = .02). The ability of H48 AUC for sVCAM-1 to discriminate between patients with or without the composite endpoint was evaluated using receiver operating characteristics with an AUC at 0.67 (0.57-0.78, p = .004). This ability was significantly superior to H48 AUC creatine kinase (p = .03).
Conclusions: In STEMI patients, high sVCAM-1 levels are associated with a poor clinical outcome. sVCAM-1 is an early postmyocardial infarction biomarker and might be an interesting target for the development of future therapeutic strategies.
Keywords: STEMI; VCAM-1; acute coronary syndrome; cell adhesion molecules; inflammation.
© 2021 The Authors. Immunity, Inflammation and Disease published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Usefulness of High Sensitivity Troponin T to Predict Long-Term Left Ventricular Dysfunction After ST-Elevation Myocardial Infarction.Am J Cardiol. 2020 Nov 1;134:8-13. doi: 10.1016/j.amjcard.2020.07.060. Epub 2020 Aug 15. Am J Cardiol. 2020. PMID: 32933755
-
High Serum Secreted Frizzled-Related Protein 5 Levels Associates with Early Improvement of Cardiac Function Following ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction Treated by Primary Percutaneous Coronary Intervention.J Atheroscler Thromb. 2019 Oct 1;26(10):868-878. doi: 10.5551/jat.47019. Epub 2019 Feb 15. J Atheroscler Thromb. 2019. PMID: 30773518 Free PMC article.
-
The contemporary value of peak creatine kinase-MB after ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction above other clinical and angiographic characteristics in predicting infarct size, left ventricular ejection fraction, and mortality.Clin Cardiol. 2017 May;40(5):322-328. doi: 10.1002/clc.22663. Epub 2016 Dec 27. Clin Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 28026027 Free PMC article.
-
Influencing factors and prognostic value of left ventricular systolic dysfunction in patients with complete occlusion of the left anterior descending artery reperfused by primary percutaneous coronary intervention.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2023 Jul 10;23(1):344. doi: 10.1186/s12872-023-03341-5. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2023. PMID: 37430213 Free PMC article.
-
[Comparison of the predictive value of the modified CADILLAC, GRACE and TIMI risk scores for the risk of short-term death in patients with acute ST segment elevation myocardial infarction after percutaneous coronary intervention].Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2023 Mar;35(3):299-304. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn121430-20220727-00696. Zhonghua Wei Zhong Bing Ji Jiu Yi Xue. 2023. PMID: 36916344 Chinese.
Cited by
-
Endothelitis profile in acute heart failure and cardiogenic shock patients: Endocan as a potential novel biomarker and putative therapeutic target.Front Physiol. 2022 Aug 11;13:965611. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2022.965611. eCollection 2022. Front Physiol. 2022. PMID: 36035482 Free PMC article.
-
Colchicine in acute myocardial infarction: cardiovascular events at 1-year follow up.Open Heart. 2024 Jan 17;11(1):e002474. doi: 10.1136/openhrt-2023-002474. Open Heart. 2024. PMID: 38233042 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
The Impact of VCAM-1 expression on left ventricular performance following acute coronary syndromes.J Med Life. 2025 May;18(5):509-514. doi: 10.25122/jml-2025-0083. J Med Life. 2025. PMID: 40599142 Free PMC article.
-
CMRSegTools: An open-source software enabling reproducible research in segmentation of acute myocardial infarct in CMR images.PLoS One. 2022 Sep 13;17(9):e0274491. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0274491. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36099286 Free PMC article.
-
Elevated Inflammation and Adhesion Molecule hsCRP, GDF-15 and VCAM-1 in Angina Patients with Non-obstructive Coronary Artery Disease.Malays J Med Sci. 2024 Dec;31(6):148-159. doi: 10.21315/mjms2024.31.6.12. Epub 2024 Dec 31. Malays J Med Sci. 2024. PMID: 39830114 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

