Lipopolysaccharide Administration Alters Extracellular Vesicles in Cell Lines and Mice
- PMID: 33559732
- PMCID: PMC7952295
- DOI: 10.1007/s00284-021-02348-5
Lipopolysaccharide Administration Alters Extracellular Vesicles in Cell Lines and Mice
Abstract
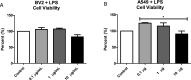
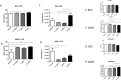
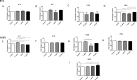
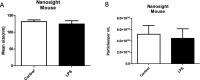
Extracellular vesicles (EVs) play a fundamental role in cell and infection biology and have the potential to act as biomarkers for novel diagnostic tools. In this study, we explored the in vitro impact of bacterial lipopolysaccharide administration on cell lines that represents a target for bacterial infection in the host. Administration of lipopolysaccharide at varying concentrations to A549 and BV-2 cell lines caused only modest changes in cell death, but EV numbers were significantly changed. After treatment with the highest concentration of lipopolysaccharide, EVs derived from A549 cells packaged significantly less interleukin-6 and lysosomal-associated membrane protein 1. EVs derived from BV-2 cells packaged significantly less tumor necrosis factor after administration of lipopolysaccharide concentrations of 0.1 µg/mL and 1 µg/mL. We also examined the impact of lipopolysaccharide administration on exosome biogenesis and cargo composition in BALB/c mice. Serum-isolated EVs from lipopolysaccharide-treated mice showed significantly increased lysosomal-associated membrane protein 1 and toll-like receptor 4 levels compared with EVs from control mice. In summary, this study demonstrated that EV numbers and cargo were altered using these in vitro and in vivo models of bacterial infection.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest in participating in this research. The funders had no role in the study design, data collection and analysis, decision to publish, or preparation of the manuscript.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inflammation leads to distinct populations of extracellular vesicles from microglia.J Neuroinflammation. 2018 May 28;15(1):168. doi: 10.1186/s12974-018-1204-7. J Neuroinflammation. 2018. PMID: 29807527 Free PMC article.
-
Beta cell extracellular vesicle miR-21-5p cargo is increased in response to inflammatory cytokines and serves as a biomarker of type 1 diabetes.Diabetologia. 2018 May;61(5):1124-1134. doi: 10.1007/s00125-018-4559-5. Epub 2018 Feb 14. Diabetologia. 2018. PMID: 29445851 Free PMC article.
-
Cellular senescence contributes to age-dependent changes in circulating extracellular vesicle cargo and function.Aging Cell. 2020 Mar;19(3):e13103. doi: 10.1111/acel.13103. Epub 2020 Jan 21. Aging Cell. 2020. PMID: 31960578 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicles in Essential Hypertension: Hidden Messengers.Curr Hypertens Rep. 2020 Sep 3;22(10):76. doi: 10.1007/s11906-020-01084-8. Curr Hypertens Rep. 2020. PMID: 32880744 Review.
-
Extracellular vesicles and their nucleic acids for biomarker discovery.Pharmacol Ther. 2018 Dec;192:170-187. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2018.08.002. Epub 2018 Aug 3. Pharmacol Ther. 2018. PMID: 30081050 Review.
Cited by
-
Canine Coronavirus Infection Modulates the Biogenesis and Composition of Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles.Biomedicines. 2023 Mar 21;11(3):976. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines11030976. Biomedicines. 2023. PMID: 36979955 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Roles of Extracelluar Vesicles Derived from Bacteria, Mammalian or Plant Cells in the Pathogenesis and Clinical Application of Neurodegenerative Diseases.Biomolecules. 2024 Mar 6;14(3):312. doi: 10.3390/biom14030312. Biomolecules. 2024. PMID: 38540732 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human Adenovirus Serotype 3 Infection Modulates the Biogenesis and Composition of Lung Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles.J Immunol Res. 2021 Dec 9;2021:2958394. doi: 10.1155/2021/2958394. eCollection 2021. J Immunol Res. 2021. PMID: 34926703 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicles Cargo in Modulating Microglia Functional Responses.Biology (Basel). 2022 Sep 29;11(10):1426. doi: 10.3390/biology11101426. Biology (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36290330 Free PMC article.
-
Membrane Vesicles Derived from Gut Microbiota and Probiotics: Cutting-Edge Therapeutic Approaches for Multidrug-Resistant Superbugs Linked to Neurological Anomalies.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Nov 3;14(11):2370. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14112370. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36365188 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

