Inline Liquid Chromatography-Fast Photochemical Oxidation of Proteins for Targeted Structural Analysis of Conformationally Heterogeneous Mixtures
- PMID: 33560821
- PMCID: PMC7951798
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.analchem.0c04872
Inline Liquid Chromatography-Fast Photochemical Oxidation of Proteins for Targeted Structural Analysis of Conformationally Heterogeneous Mixtures
Abstract
Structural analysis of proteins in a conformationally heterogeneous mixture has long been a difficult problem in structural biology. In structural analysis by covalent labeling mass spectrometry, conformational heterogeneity results in data reflecting a weighted average of all conformers, complicating data analysis and potentially causing misinterpretation of results. Here, we describe a method coupling size-exclusion chromatography (SEC) with hydroxyl radical protein footprinting using inline fast photochemical oxidation of proteins (FPOP). Using a controlled synthetic mixture of holomyoglobin and apomyoglobin, we validate that we can achieve accurate footprints of each conformer using LC-FPOP when compared to offline FPOP of each pure conformer. We then applied LC-FPOP to analyze the adalimumab heat-shock aggregation process. We found that the LC-FPOP footprint of unaggregated adalimumab was consistent with a previously published footprint of the native IgG. The LC-FPOP footprint of the aggregation product indicated that heat-shock aggregation primarily protected the hinge region, suggesting that this region is involved with the heat-shock aggregation process of this molecule. LC-FPOP offers a new method to probe dynamic conformationally heterogeneous mixtures that can be separated by SEC such as biopharmaceutical aggregates and to obtain accurate information on the topography of each conformer.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest Disclosure
J.S.S. discloses a significant financial interest in GenNext Technologies, Inc., a small company seeking to commercialize technologies for protein higher-order structure analysis.
Figures

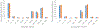
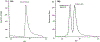
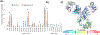
References
-
- Hambly DM; Gross ML Laser flash photolysis of hydrogen peroxide to oxidize protein solvent-accessible residues on the microsecond timescale. J Am Soc Mass Spectrom 2005, 16, 2057–2063. - PubMed
-
- Buxton GV; Greenstock CL; Helman WP; Ross AB Critical Review of rate constants for reactions of hydrated electrons, hydrogen atoms and hydroxyl radicals (·OH/·O− in Aqueous Solution. Journal of Physical and Chemical Reference Data 1988, 17, 513–886.
-
- Xu G; Chance MR Radiolytic modification and reactivity of amino acid residues serving as structural probes for protein footprinting. Anal Chem 2005, 77, 4549–4555. - PubMed
-
- Chance MR Unfolding of apomyoglobin examined by synchrotron footprinting. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2001, 287, 614–621. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

