The Value of Early Tumor Size Response to Chemotherapy in Pediatric Rhabdomyosarcoma
- PMID: 33561094
- PMCID: PMC7866196
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers13030510
The Value of Early Tumor Size Response to Chemotherapy in Pediatric Rhabdomyosarcoma
Abstract
Rhabdomyosarcoma is the most common soft tissue sarcoma in childhood. Results of clinical trials, with three-year event-free and overall survival as primary outcomes, often take 7 to 10 years. Identification of an early surrogate biomarker, predictive for survival, is therefore crucial. We conducted a systematic review to define the prognostic value of early tumor size response in children with IRSG group III rhabdomyosarcoma. The search included MEDLINE/EMBASE from inception to 18 November 2020. In total, six studies were included, describing 2010 patients, and assessed by the Quality in Prognosis Studies (QUIPS) instrument. Four studies found no prognostic value for tumor size response, whereas two studies reported a prognostic effect. In these two studies, the survival rate of patients with progressive disease was not separately analyzed from patients with stable disease, potentially explaining the difference in study outcome. In conclusion, our findings support that early progression of disease is associated with poorer survival, justifying adaptation of therapy. However, in patients with non-progressive disease, there is no evidence that the degree of response is a prognostic marker for survival. Because the vast majority of patients do not have progressive disease, early tumor size response should be reconsidered for assessment of treatment efficacy. Therefore, at present, early surrogate biomarkers for survival are still lacking.
Keywords: biomarker; prognosis; response; rhabdomyosarcoma; sarcoma.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures
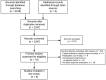
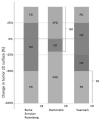
References
-
- Bisogno G., Jenney M., Bergeron C., Melcón S.G., Ferrari A., Oberlin O., Carli M., Stevens M., Kelsey A., De Paoli A., et al. Addition of dose-intensified doxorubicin to standard chemotherapy for rhabdomyosarcoma (EpSSG RMS 2005): A multicentre, open-label, randomised controlled, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 2018;19:1061–1071. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(18)30337-1. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Arndt C.A., Stoner J.A., Hawkins D.S., Rodeberg D.A., Hayes-Jordan A.A., Paidas C.N., Parham D.M., Teot L.A., Wharam M.D., Breneman J.C., et al. Vincristine, actinomycin, and cyclophosphamide compared with vincristine, actinomycin, and cyclophosphamide alternating with vincristine, topotecan, and cyclophosphamide for intermediate-risk rhabdomyosarcoma: Children’s oncology group study D9803. J. Clin. Oncol. 2009;27:5182–5188. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2009.22.3768. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chisholm J.C., Marandet J., Rey A., Scopinaro M., De Toledo J.S., Merks J.H.M., O‘Meara A., Stevens M.C.G., Oberlin O. Prognostic Factors After Relapse in Nonmetastatic Rhabdomyosarcoma: A Nomogram to Better Define Patients Who Can Be Salvaged with Further Therapy. J. Clin. Oncol. 2011;29:1319–1325. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2010.32.1984. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

