Simultaneously targeting cancer-associated fibroblasts and angiogenic vessel as a treatment for TNBC
- PMID: 33561195
- PMCID: PMC7876552
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20200712
Simultaneously targeting cancer-associated fibroblasts and angiogenic vessel as a treatment for TNBC
Abstract
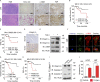
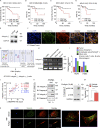
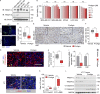
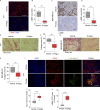
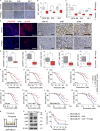
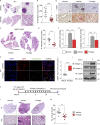
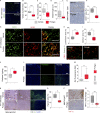
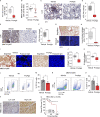
Fibrotic tumor stroma plays an important role in facilitating triple-negative breast cancer (TNBC) progression and chemotherapeutic resistance. We previously reported a rationally designed protein (ProAgio) that targets integrin αvβ3 at a novel site. ProAgio induces apoptosis via the integrin. Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) and angiogenic endothelial cells (aECs) in TNBC tumor express high levels of integrin αvβ3. ProAgio effectively induces apoptosis in CAFs and aECs. The depletion of CAFs by ProAgio reduces intratumoral collagen and decreases growth factors released from CAFs in the tumor, resulting in decreased cancer cell proliferation and apoptotic resistance. ProAgio also eliminates leaky tumor angiogenic vessels, which consequently reduces tumor hypoxia and improves drug delivery. The depletion of CAFs and reduction in hypoxia by ProAgio decreases lysyl oxidase (LOX) secretion, which may play a role in the reduction of metastasis. ProAgio stand-alone or in combination with a chemotherapeutic agent provides survival benefit in TNBC murine models, highlighting the therapeutic potential of ProAgio as a treatment strategy.
© 2021 Sharma et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: L. Sun reported he owns shares in Amoytop, which exclusively licenses the commercial right of ProAgio in the Chinese market. Z.-R. Liu reported "other" from ProDa BioTech LLC outside the submitted work; in addition, Z.-R. Liu had a patent number 9,175,063 licensed to ProDa BioTech LLC. No other disclosures were reported.
Figures






References
-
- Antonyak, M.A., Miller A.M., Jansen J.M., Boehm J.E., Balkman C.E., Wakshlag J.J., Page R.L., and Cerione R.A.. 2004. Augmentation of tissue transglutaminase expression and activation by epidermal growth factor inhibit doxorubicin-induced apoptosis in human breast cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 279:41461–41467. 10.1074/jbc.M404976200 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Attieh, Y., Clark A.G., Grass C., Richon S., Pocard M., Mariani P., Elkhatib N., Betz T., Gurchenkov B., and Vignjevic D.M.. 2017. Cancer-associated fibroblasts lead tumor invasion through integrin-β3-dependent fibronectin assembly. J. Cell Biol. 216:3509–3520. 10.1083/jcb.201702033 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baumgartner, G., Gomar-Höss C., Sakr L., Ulsperger E., and Wogritsch C.. 1998. The impact of extracellular matrix on the chemoresistance of solid tumors--experimental and clinical results of hyaluronidase as additive to cytostatic chemotherapy. Cancer Lett. 131:85–99. 10.1016/S0304-3835(98)00204-3 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

