Leadership Styles and Nurses' Job Satisfaction. Results of a Systematic Review
- PMID: 33562016
- PMCID: PMC7915070
- DOI: 10.3390/ijerph18041552
Leadership Styles and Nurses' Job Satisfaction. Results of a Systematic Review
Abstract
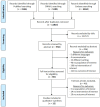
Healthcare organisations are social systems in which human resources are the most important factor. Leadership plays a key role, affecting outcomes for professionals, patients and work environment. The aim of this research was to identify and analyse the knowledge present to date concerning the correlation between leadership styles and nurses' job satisfaction. A systematic review was carried out on PubMed, CINAHL and Embase using the following inclusion criteria: impact of different leadership styles on nurses' job satisfaction; secondary care; nursing setting; full-text available; English or Italian language. From 11,813 initial titles, 12 studies were selected. Of these, 88% showed a significant correlation between leadership style and nurses' job satisfaction. Transformational style had the highest number of positive correlations followed by authentic, resonant and servant styles. Passive-avoidant and laissez-faire styles, instead, showed a negative correlation with job satisfaction in all cases. Only the transactional style showed both positive and negative correlation. In this challenging environment, leaders need to promote technical and professional competencies, but also act to improve staff satisfaction and morale. It is necessary to identify and fill the gaps in leadership knowledge as a future objective to positively affect health professionals' job satisfaction and therefore healthcare quality indicators.
Keywords: job satisfaction; leadership; nursing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Frisicale E.M., Grossi A., Cacciatore P., Carini E., Villani L., Pezzullo A.M., Gentili A., Cabral M., Silenzi A., Favaretti C., et al. The need of leadership in managing healthcare and policy-making. G. Ital. Health Technol. Assess. 2019;12(Suppl. S2):1–13.
-
- Rad A.M.M., Yarmohammadian H.M. A Study of Relationship between Managers’ Leadership Style and employees’ Job Satisfaction. Leadersh. Health Serv. 2006;19:11–28. - PubMed
-
- Cohen W.A. The Art of a Leader. Prentice Hall; Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA: 1990.
-
- Middlehurst R. Not enough science or not enough learning? Exploring the gaps between leadership theory and practice. High. Educ. Q. 2008;62:322–339. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-2273.2008.00397.x. - DOI
-
- Burns J.M. Leadership. Harper & Row; New York, NJ, USA: 1978.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources