Recent Achievements in Dyes Removal Focused on Advanced Oxidation Processes Integrated with Biological Methods
- PMID: 33562176
- PMCID: PMC7914684
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules26040870
Recent Achievements in Dyes Removal Focused on Advanced Oxidation Processes Integrated with Biological Methods
Abstract
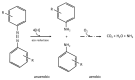
In the last 3 years alone, over 10,000 publications have appeared on the topic of dye removal, including over 300 reviews. Thus, the topic is very relevant, although there are few articles on the practical applications on an industrial scale of the results obtained in research laboratories. Therefore, in this review, we focus on advanced oxidation methods integrated with biological methods, widely recognized as highly efficient treatments for recalcitrant wastewater, that have the best chance of industrial application. It is extremely important to know all the phenomena and mechanisms that occur during the process of removing dyestuffs and the products of their degradation from wastewater to prevent their penetration into drinking water sources. Therefore, particular attention is paid to understanding the mechanisms of both chemical and biological degradation of dyes, and the kinetics of these processes, which are important from a design point of view, as well as the performance and implementation of these operations on a larger scale.
Keywords: AOPs; biological processes; decolorization; dyes and pigments; textile wastewater.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Gupta V.K. Fundamentals of Natural Dyes and Its Application on Textile Substrates. In: Samanta A.K., Awwad N.S., Algarni H.M., editors. Chemistry and Technology of Natural and Synthetic Dyes and Pigments. IntechOpen; London, UK: 2020.
-
- Dyes And Pigments Market Size. Volume 130 Mordor Intelligence; Hyderabad, India: 2020. Industry Report 2020–2027.
-
- Yuan H., Chen L., Cao Z., Hong F.F. Enhanced decolourization efficiency of textile dye Reactive Blue 19 in a horizontal rotating reactor using strips of BNC-immobilized laccase: Optimization of conditions and comparison of decolourization efficiency. Biochem. Eng. J. 2020;156:107501. doi: 10.1016/j.bej.2020.107501. - DOI
-
- Albahnasawi A., Yüksel E., Gürbulak E., Duyum F. Fate of aromatic amines through decolorization of real textile wastewater under anoxic-aerobic membrane bioreactor. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2020;8:104226. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2020.104226. - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources