Viral Infection and Cardiovascular Disease: Implications for the Molecular Basis of COVID-19 Pathogenesis
- PMID: 33562193
- PMCID: PMC7914972
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22041659
Viral Infection and Cardiovascular Disease: Implications for the Molecular Basis of COVID-19 Pathogenesis
Abstract
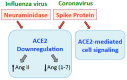
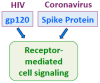
The current pandemic of coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is caused by severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). While this respiratory virus only causes mild symptoms in younger healthy individuals, elderly people and those with cardiovascular diseases such as systemic hypertension are susceptible to developing severe conditions that can be fatal. SARS-CoV-2 infection is also associated with an increased incidence of cardiovascular diseases such as myocardial injury, acute coronary syndrome, and thromboembolism. Understanding the mechanisms of the effects of this virus on the cardiovascular system should thus help develop therapeutic strategies to reduce the mortality and morbidity associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection. Since this virus causes severe and fatal conditions in older individuals with cardiovascular comorbidities, effective therapies targeting specific populations will likely contribute to ending this pandemic. In this review article, the effects of various viruses-including other coronaviruses, influenza, dengue, and human immunodeficiency virus-on the cardiovascular system are described to help provide molecular mechanisms of pathologies associated with SARS-CoV-2 infection and COVID-19. The goal is to provide mechanistic information from the biology of other viral infections in relation to cardiovascular pathologies for the purpose of developing improved vaccines and therapeutic agents effective in preventing and/or treating the acute and long-term consequences of SARS-CoV-2 and COVID-19.
Keywords: ACE2; COVID-19; HIV; cardiovascular; coronavirus; dengue; heart; influenza; spike protein; virus.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
Figures


References
-
- Wu C., Chen X., Cai Y., Xia J., Zhou X., Xu S., Huang H., Zhang L., Zhou X., Du C., et al. Risk factors associated with acute respiratory distress syndrome and death in patients with coronavirus disease 2019 pneumonia in Wuhan, China. JAMA Intern. Med. 2020;180:e200994. doi: 10.1001/jamainternmed.2020.0994. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Tai W., He L., Zhang X., Pu J., Voronin D., Jiang S., Zhou Y., Du L. Characterization of the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of 2019 novel coronavirus: Implication for development of RBD protein as a viral attachment inhibitor and vaccine. Cell. Mol. Immunol. 2020;17:613–620. doi: 10.1038/s41423-020-0400-4. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hoffmann M., Kleine-Weber H., Schroeder S., Krüger N., Herrler T., Erichsen S., Schiergens T.S., Herrler G., Wu N.H., Nitsche A., et al. SARS-CoV-2 cell entry depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and is blocked by a clinically proven protease inhibitor. Cell. 2020;181:271–280.e8. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2020.02.052. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

