Prevalence and Determinants of Medication Adherence among Patients with HIV/AIDS in Southern Vietnam
- PMID: 33562451
- PMCID: PMC7931092
- DOI: 10.3390/idr13010014
Prevalence and Determinants of Medication Adherence among Patients with HIV/AIDS in Southern Vietnam
Abstract
This study was conducted to determine the prevalence and determinants of medication adherence among patients with HIV/AIDS in southern Vietnam.
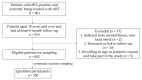
Methods: A cross-sectional study was conducted in a hospital in southern Vietnam from June to December 2019 on patients who began antiretroviral therapy (ART) for at least 6 months. Using a designed questionnaire, patients were considered adherent if they took correct medicines with right doses, on time and properly with food and beverage and had follow-up visits as scheduled. Multivariable logistic regression was used to identify determinants of adherence.
Key findings: A total of 350 patients (from 861 medical records) were eligible for the study. The majority of patients were male (62.9%), and the dominant age group (≥35 years old) accounted for 53.7% of patients. Sexual intercourse was the primary route of transmission of HIV (95.1%). The proportions of participants who took the correct medicine and at a proper dose were 98.3% and 86.3%, respectively. In total, 94.9% of participants took medicine appropriately in combination with food and beverage, and 75.7% of participants were strictly adherent to ART. The factors marital status (odds ratio (OR) = 2.54; 95%CI = 1.51-4.28), being away from home (OR = 1.7; 95%CI = 1.03-2.78), substance abuse (OR = 2.7; 95%CI = 1.44-5.05), general knowledge about ART (OR = 2.75; 95%CI = 1.67-4.53), stopping medication after improvement (OR = 4.16; 95%CI = 2.29-7.56) and self-assessment of therapy adherence (OR = 9.83; 95%CI = 5.44-17.77) were significantly associated with patients' adherence.
Conclusions: Three-quarters of patients were adherent to ART. Researchers should consider these determinants of adherence in developing interventions in further studies.
Keywords: Vietnam; acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS); antiretroviral therapy (ART); human immunodeficiency virus (HIV); medication adherence.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
References
-
- Global HIV & AIDS Statistics—2020 Fact Sheet. Unaids.org. [(accessed on 12 August 2020)]; Available online: https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/fact-sheet.
-
- UNAIDS Data 2020. Unaids.org. [(accessed on 12 August 2020)]; Available online: https://www.unaids.org/en/resources/documents/2020/unaids-data.
-
- Vietnam Ministry of Health . Report on Results of HIV/AIDS Prevention and Control in 2019 and Key Tasks in 2020. Vietnam Ministry of Health; Hanoi, Vietnam: 2020.
-
- Schaecher K.L. The importance of treatment adherence in HIV. Am. J. Manag. Care. 2013;19(Suppl. 12):s231–s237. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources