Modernizing Clinical Trial Eligibility Criteria: Recommendations of the ASCO-Friends of Cancer Research Prior Therapies Work Group
- PMID: 33563637
- PMCID: PMC8170959
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-20-3854
Modernizing Clinical Trial Eligibility Criteria: Recommendations of the ASCO-Friends of Cancer Research Prior Therapies Work Group
Abstract
Purpose: Restrictive eligibility criteria induce differences between clinical trial and "real-world" treatment populations. Restrictions based on prior therapies are common; minimizing them when appropriate may increase patient participation in clinical trials.
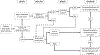
Experimental design: A multi-stakeholder working group developed a conceptual framework to guide evaluation of prevailing practices with respect to using prior treatment as selection criteria for clinical trials. The working group made recommendations to minimize restrictions based on prior therapies within the boundaries of scientific validity, patient centeredness, distributive justice, and beneficence.
Recommendations: (i) Patients are eligible for clinical trials regardless of the number or type of prior therapies and without requiring a specific therapy prior to enrollment unless a scientific or clinically based rationale is provided as justification. (ii) Prior therapy (either limits on number and type of prior therapies or requirements for specific therapies before enrollment) could be used to determine eligibility in the following cases: a) the agents being studied target a specific mechanism or pathway that could potentially interact with a prior therapy; b) the study design requires that all patients begin protocol-specified treatment at the same point in the disease trajectory; and c) in randomized clinical studies, if the therapy in the control arm is not appropriate for the patient due to previous therapies received. (iii) Trial designers should consider conducting evaluation separately from the primary endpoint analysis for participants who have received prior therapies.
Conclusions: Clinical trial sponsors and regulators should thoughtfully reexamine the use of prior therapy exposure as selection criteria to maximize clinical trial participation.See related commentary by Giantonio, p. 2369.
©2021 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures
Comment in
-
Eligibility in Cancer Clinical Research: The Intersection of Discovery, Generalizability, Beneficence, and Justice.Clin Cancer Res. 2021 May 1;27(9):2369-2371. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-21-0085. Epub 2021 Feb 18. Clin Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 33602680
References
-
- Heymach J, Krilov L, Alberg A, Baxter N, Chang SM, Corcoran RB, et al. Clinical Cancer Advances 2018: Annual Report on Progress Against Cancer From the American Society of Clinical Oncology. J Clin Oncol [Internet]. American Society of Clinical Oncology; 2018;36:1020–44. Available from: 10.1200/JCO.2017.77.0446 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Fontes Jardim DL, Schwaederle M, Wei C, Lee JJ, Hong DS, Eggermont AM, et al. Impact of a Biomarker-Based Strategy on Oncology Drug Development: A Meta-Analysis of Clinical Trials Leading to FDA Approval. JNCI J Natl Cancer Inst [Internet]. 2015;107. Available from: 10.1093/jnci/djv253 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhang S, Anjum R, Squillace R, Nadworny S, Zhou T, Keats J, et al. The Potent ALK Inhibitor Brigatinib (AP26113) Overcomes Mechanisms of Resistance to First- and Second-Generation ALK Inhibitors in Preclinical Models. Clin Cancer Res [Internet]. 2016; Available from: http://clincancerres.aacrjournals.org/content/early/2016/10/21/1078-0432... - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

