Steroid receptor coactivator 3 (SRC-3/AIB1) is enriched and functional in mouse and human Tregs
- PMID: 33564037
- PMCID: PMC7873281
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-021-82945-3
Steroid receptor coactivator 3 (SRC-3/AIB1) is enriched and functional in mouse and human Tregs
Abstract
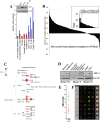
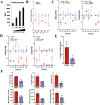
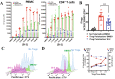
A subset of CD4 + lymphocytes, regulatory T cells (Tregs), are necessary for central tolerance and function as suppressors of autoimmunity against self-antigens. The SRC-3 coactivator is an oncogene in multiple cancers and is capable of potentiating numerous transcription factors in a wide variety of cell types. Src-3 knockout mice display broad lymphoproliferation and hypersensitivity to systemic inflammation. Using publicly available bioinformatics data and directed cellular approaches, we show that SRC-3 also is highly enriched in Tregs in mice and humans. Human Tregs lose phenotypic characteristics when SRC-3 is depleted or pharmacologically inhibited, including failure of induction from resting T cells and loss of the ability to suppress proliferation of stimulated T cells. These data support a model for SRC-3 as a coactivator that actively participates in protection from autoimmunity and may support immune evasion of cancers by contributing to the biology of Tregs.
Conflict of interest statement
BCN, PJ, BY, QF, SD, DML, and BWO all hold stock in a virtual company created within Baylor College of Medicine that has no commercial funding. DLC and NJM declare no financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- Guan, X. Y. et al. Hybrid selection of transcribed sequences from microdissected DNA: isolation of genes within amplified region at 20q11-q13.2 in breast cancer. Cancer Res.56, 3446–3450 (1996). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

