Ocular surface squamous neoplasia: management and outcomes
- PMID: 33564137
- PMCID: PMC8169825
- DOI: 10.1038/s41433-021-01422-3
Ocular surface squamous neoplasia: management and outcomes
Abstract
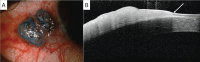
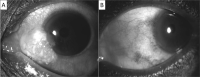
Ocular surface squamous neoplasia (OSSN) is the most common ocular tumour with an incidence ranging from 0.03 to 1.9 per 100,000 persons/year. The diagnosis is made on clinical suspicion and confirmed with anterior-segment optical coherence tomography (AS-OCT), cytology, or histology. The purpose of this review is to provide an overview of the management options available for OSSN and review their success and recurrence rates. Surgery is the gold standard for the management of small OSSN lesions. With the increased use of less invasive diagnostic modalities such as AS-OCT and cytology, there has been a move to use topical therapies for the management of OSSN. The most commonly used agents are interferon-α2b (IFN), mitomycin-C (MMC) and 5-fluorouracil (5FU). They have been shown to have similar resolution and recurrence rates but differ in cost and side effect profile. IFN has the lowest side effect profile, but is also the most expensive, whereas MMC has the greatest surface toxicity and is priced midway between the three. 5FU is the cheapest of the three topical agents with less surface toxicity than MMC. Radiotherapy is mostly employed as adjuvant therapy. Newer novel therapies are available but have not been widely adopted as mainstream therapy due to cost and lack of clinical evidence. OSSN has the benefit of many management options. No single modality has been shown to superior and some patients will need the use of combination therapy to achieve an optimal clinical outcome.
摘要: 眼表鳞状细胞癌 (Ocular surface squamous neoplasia, OSSN) 是最常见的眼部肿瘤, 发病率为0.031.9 / 10万人/年。临床表现疑似的病例, 进一步由前节相干光断层扫描 (anterior-segment optical coherence tomography, AS-OCT) 、细胞学或组织学进行确诊。本综述的目的是针对OSSN可行的治疗策略进行概述, 并阐述它们的成功率和复发率。手术是治疗小病灶OSSN治疗的金标准。随着AS-OCT和细胞学等侵入性较低的诊断方法的使用越来越多, 局部滴用眼药的治疗OSSN已经成为一种趋势。最常用的药物是干扰素-α2b (interferon-α2b, IFN)、丝裂霉素- c (mitomycin-C, MMC)和5-氟尿嘧啶(5-fluorouracil, 5FU)。它们具有相似的治疗率和复发率, 但在成本和副作用方面有所不同。IFN的副作用最低, 但也是最贵的, 而MMC的表面毒性最大, 价格介于三种药物之间。5FU是三种眼药中最便宜的, 表面毒性较MMC小。放射治疗主要用于辅助治疗。新的治疗手段是可行的, 但由于成本及缺乏临床证据, 并没有被广泛采用作为主流疗法。OSSN受益于许多治疗以及管理策略。没有一种单一的治疗方式显示出优越性, 一些患者需要使用联合治疗以达到最佳的临床结局。.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Hollhumer R, Williams S, Michelow P Ocular surface squamous neoplasia: Population demographics, pathogenesis and risk factors. Afr. Vis. Eye Health. 2020; 79. Available at: http://www.avehjournal.org/index.php/AVEH/article/view/553 [Accessed June 23, 2020].
-
- Stone DU, Butt AL, Chodosh J. Ocular surface squamous neoplasia: a standard of care survey. Cornea. 2005;24:297–300. doi: 10.1097/01.ico.0000138834.42489.ba. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

