A review on COVID-19 forecasting models
- PMID: 33564213
- PMCID: PMC7861008
- DOI: 10.1007/s00521-020-05626-8
A review on COVID-19 forecasting models
Abstract
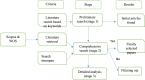
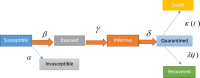
The novel coronavirus (COVID-19) has spread to more than 200 countries worldwide, leading to more than 36 million confirmed cases as of October 10, 2020. As such, several machine learning models that can forecast the outbreak globally have been released. This work presents a review and brief analysis of the most important machine learning forecasting models against COVID-19. The work presented in this study possesses two parts. In the first section, a detailed scientometric analysis presents an influential tool for bibliometric analyses, which were performed on COVID-19 data from the Scopus and Web of Science databases. For the above-mentioned analysis, keywords and subject areas are addressed, while the classification of machine learning forecasting models, criteria evaluation, and comparison of solution approaches are discussed in the second section of the work. The conclusion and discussion are provided as the final sections of this study.
Keywords: Analysis; COVID-19; Forecasting; SEIR; SIR; Time series.
© The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer-Verlag London Ltd. part of Springer Nature 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures




References
-
- Putra S, Khozin Mutamar Z. Estimation of parameters in the SIR epidemic model using particle swarm optimization. Am J Math Comput Model. 2019;4(4):83–93. doi: 10.11648/j.ajmcm.20190404.11. - DOI
-
- Mbuvha RR, Marwala T (2020) On data-driven management of the COVID-19 outbreak in South Africa. medRxiv
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
