Gadolinium Chloride Inhibits the Production of Liver Interleukin-27 and Mitigates Liver Injury in the CLP Mouse Model
- PMID: 33564275
- PMCID: PMC7867451
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/2605973
Gadolinium Chloride Inhibits the Production of Liver Interleukin-27 and Mitigates Liver Injury in the CLP Mouse Model
Abstract
Background: Liver macrophages play an important regulatory role in the inflammatory response of liver injury after severe infection. Interleukin- (IL-) 27 is an inflammatory cytokine that plays an important role in diseases caused by bacterial infection. However, the relationship between IL-27 and liver macrophages in liver injury after severe infection is not yet clear.
Methods: A cecal ligation puncture (CLP) model was established in wild-type (WT) and IL-27 receptor- (WSX-1-) deficient (IL-27r-/-) mice, and recombinant IL-27 and gadolinium chloride (GdCl3) were injected into WT mice in the designated groups. The serum and liver IL-27, IL-6, tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF-α), and IL-1β expression levels were evaluated by ELISA, quantitative PCR, or Western blotting; serum ALT and AST were detected by detection kits; and the severity of liver damage was evaluated by hematoxylin and eosin staining and the TUNEL assay of the liver tissue from the different groups. Liver macrophage polarization was evaluated by immunofluorescence. In addition, the polarization of peritoneal macrophage was evaluated by flow cytometry.
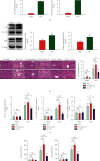
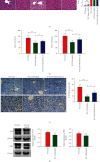
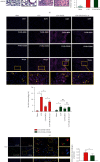
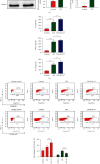
Results: The serum and liver IL-27 expression levels were elevated in WT mice after CLP-induced severe infection, which were consistent with the changes in HE scores in the liver tissue. The levels of serum ALT, AST, liver IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-1β mRNA and liver pathological injury scores were further increased when pretreated with recombinant IL-27 in WT mice, but these levels were decreased in IL-27r-/- mice after CLP-induced severe infection compared to WT mice. In WT mice pretreated with GdCl3, liver pathological scores, serum ALT and AST, TUNEL-positive cell proportion from liver tissues, liver IL-27 expression, and the liver macrophages M1 polarization proportion decreased after CLP; however, the serum IL-27, IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-1β levels and the pathological lung and kidney scores were not significantly changed. When supplemented with exogenous IL-27, the liver pathological scores, serum ALT, AST, TUNEL-positive cell proportion of liver tissues, liver IL-27 expression, and the liver macrophage M1 polarization proportion increased. The in vitro, IL-27 expression increased in peritoneal macrophages when stimulated with LPS. Recombinant IL-27 together with LPS promoted the elevations in IL-6, TNF-α, and IL-1β levels in supernatant and the M1 polarization of peritoneal macrophages.
Conclusion: IL-27 is an important cytokine in the inflammatory response to liver injury after severe infection. The reduction of liver injury by gadolinium chloride in severe infection mice models may relate to the inhibition of liver IL-27 production. These changes may be mainly related to the decrease of liver macrophages M1 polarization. IL-27 may have a positive feedback on these macrophages.
Copyright © 2021 Jing Fan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
IL-27 is elevated in sepsis with acute hepatic injury and promotes hepatic damage and inflammation in the CLP model.Cytokine. 2020 Mar;127:154936. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2019.154936. Epub 2019 Nov 28. Cytokine. 2020. PMID: 31786500
-
[Effects of Krüppel-like factor 4 on inflammatory response and organ injury in septic mice].Zhonghua Shao Shang Yu Chuang Mian Xiu Fu Za Zhi. 2022 Nov 20;38(11):1047-1056. doi: 10.3760/cma.j.cn501225-20220111-00005. Zhonghua Shao Shang Yu Chuang Mian Xiu Fu Za Zhi. 2022. PMID: 36418262 Free PMC article. Chinese.
-
Diabetes exacerbated sepsis-induced intestinal injury by promoting M1 macrophage polarization via miR-3061/Snail1 signaling.Front Immunol. 2022 Sep 9;13:922614. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.922614. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36159784 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of IL-38 on Macrophages and Myocardial Ischemic Injury.Front Immunol. 2022 May 13;13:894002. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.894002. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 35634320 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the mechanism and crosstalk between IL-6 and IL- 1β on M2 macrophages under metabolic stress conditions.Cytokine. 2025 Feb;186:156852. doi: 10.1016/j.cyto.2024.156852. Epub 2025 Jan 6. Cytokine. 2025. PMID: 39765025 Review.
Cited by
-
The Predictive Role of FGF21 in Acute Liver Injury Caused by Bacterial Infectious Diseases in Critical Care: A Retrospective Cohort Study.J Inflamm Res. 2025 May 26;18:6795-6806. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S521327. eCollection 2025. J Inflamm Res. 2025. PMID: 40453967 Free PMC article.
-
Rare Earths-The Answer to Everything.Molecules. 2024 Feb 1;29(3):688. doi: 10.3390/molecules29030688. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38338432 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Biomarkers as Beacons: Illuminating Sepsis-Associated Hepato-Renal Injury.Int J Mol Sci. 2025 May 18;26(10):4825. doi: 10.3390/ijms26104825. Int J Mol Sci. 2025. PMID: 40429966 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the role of interleukin-27 as a regulator of neuronal survival in central nervous system diseases.Neural Regen Res. 2022 Oct;17(10):2149-2152. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.336134. Neural Regen Res. 2022. PMID: 35259821 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

