Characterization of Artificial Pneumothorax-Unrelated Pyothorax-Associated Lymphoma
- PMID: 33564306
- PMCID: PMC7850845
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/3869438
Characterization of Artificial Pneumothorax-Unrelated Pyothorax-Associated Lymphoma
Abstract
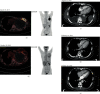
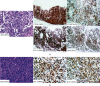
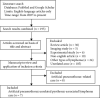
Pyothorax-associated lymphoma (PAL) is a rare disease developing from a long-term pleural cavity inflammation. Most reported PAL cases have a history of artificial pneumothorax. However, the clinical features of artificial pneumothorax-unrelated PAL remain largely unknown. Here, we reported two PAL cases diagnosed from our center in the past ten years. One case developed from asymptomatic pyothorax after pneumonectomy with a latency of 28 years, while the other case showed a relatively short latency of one year. Then we reviewed the literature of artificial pneumothorax-unrelated PAL by searching PubMed and Google Scholar from 2007. In total, nine artificial pneumothorax-unrelated PAL cases were found, predominantly in old male with median age of 76 years (ranging from 51 to 88). Most cases were diagnosed with diffuse large B-cell lymphoma (DLBCL) (n = 8, 88.9%) and had evidence of Epstein-Barr virus (EBV) infection (n = 6, 66.7%) or tuberculous pleurisy (n = 5, 55.6%). Notably, four cases (44.4%) had short intervals (no more than two years) between pleuritis and PAL. Regarding the overall survival, one-third cases survived more than 5 years after the diagnosis of PAL. In conclusion, the features of artificial pneumothorax-unrelated PAL are comparable with the classic type of PAL, except for some patients with short duration of pleuritis, and need to be identified. Treatment guideline of DLBCL is recommended for the management of PAL.
Copyright © 2021 Guang-Liang Chen et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pyothorax-associated lymphoma: a review of 106 cases.J Clin Oncol. 2002 Oct 15;20(20):4255-60. doi: 10.1200/JCO.2002.09.021. J Clin Oncol. 2002. PMID: 12377970
-
Pyothorax-associated lymphoma.Int J Hematol. 1996 Dec;65(1):9-16. doi: 10.1016/s0925-5710(96)00532-4. Int J Hematol. 1996. PMID: 8990621 Review.
-
Pyothorax-associated lymphoma: a lymphoma developing in chronic inflammation.Adv Anat Pathol. 2005 Nov;12(6):324-31. doi: 10.1097/01.pap.0000194627.50878.02. Adv Anat Pathol. 2005. PMID: 16330929 Review.
-
Pyothorax-associated lymphoma (PAL): report and review of a rare entity.Thorac Surg Sci. 2004 Oct 1;1:Doc03. Thorac Surg Sci. 2004. PMID: 21289975 Free PMC article.
-
Epstein-Barr Virus-Positive Pyothorax-Associated Lymphoma Arising from a Posttraumatic Empyema.Acta Haematol. 2015;134(3):155-60. doi: 10.1159/000380809. Epub 2015 May 5. Acta Haematol. 2015. PMID: 25968626
Cited by
-
Increased Risk of Lymphoma in Men or the Elderly Infected with Tuberculosis.Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2021 Sep 1;13(1):e2021053. doi: 10.4084/MJHID.2021.053. eCollection 2021. Mediterr J Hematol Infect Dis. 2021. PMID: 34527205 Free PMC article.
-
PD-1 inhibitors plus chemotherapy for refractory EBV-positive DLBCL: a retrospective analysis.Blood Res. 2024 Oct 30;59(1):36. doi: 10.1007/s44313-024-00042-6. Blood Res. 2024. PMID: 39475995 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting central nervous system relapse in primary breast diffuse large B-cell lymphoma using the stage-modified IPI score: A retrospective cohort study.Heliyon. 2024 Feb 21;10(5):e26795. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e26795. eCollection 2024 Mar 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38439878 Free PMC article.
-
Cancer risk in tuberculosis patients in a high endemic area.BMC Cancer. 2021 Jun 9;21(1):679. doi: 10.1186/s12885-021-08391-6. BMC Cancer. 2021. PMID: 34107921 Free PMC article.
-
EBV-positive pyothorax-associated lymphoma expresses CXCL9 and CXCL10 chemokines that attract cytotoxic lymphocytes via CXCR3.Cancer Sci. 2023 Jun;114(6):2622-2633. doi: 10.1111/cas.15782. Epub 2023 Mar 20. Cancer Sci. 2023. PMID: 36898851 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

