BioPAN: a web-based tool to explore mammalian lipidome metabolic pathways on LIPID MAPS
- PMID: 33564392
- PMCID: PMC7848852
- DOI: 10.12688/f1000research.28022.2
BioPAN: a web-based tool to explore mammalian lipidome metabolic pathways on LIPID MAPS
Abstract
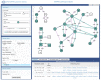
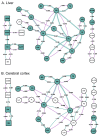
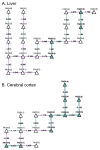
Lipidomics increasingly describes the quantification using mass spectrometry of all lipids present in a biological sample. As the power of lipidomics protocols increase, thousands of lipid molecular species from multiple categories can now be profiled in a single experiment. Observed changes due to biological differences often encompass large numbers of structurally-related lipids, with these being regulated by enzymes from well-known metabolic pathways. As lipidomics datasets increase in complexity, the interpretation of their results becomes more challenging. BioPAN addresses this by enabling the researcher to visualise quantitative lipidomics data in the context of known biosynthetic pathways. BioPAN provides a list of genes, which could be involved in the activation or suppression of enzymes catalysing lipid metabolism in mammalian tissues.
Keywords: Biosynthetic pathway analysis; LIPID MAPS; Lipidomics; lipid profiling.; lipids.
Copyright: © 2021 Gaud C et al.
Conflict of interest statement
No competing interests were disclosed.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

