Relationship between serum phosphate levels and survival in chronic hemodialysis patients: interactions with age, malnutrition and inflammation
- PMID: 33564438
- PMCID: PMC7857835
- DOI: 10.1093/ckj/sfz143
Relationship between serum phosphate levels and survival in chronic hemodialysis patients: interactions with age, malnutrition and inflammation
Abstract
Background: Evidence indicates that the inverse relationships between phosphate levels and mortality maybe modified by age. Furthermore, malnutrition and inflammation could strengthen the risk associated with phosphate abnormalities. This study aimed to assess the associations between phosphate levels and mortality while accounting for the interactions with age and parameters associated with malnutrition and inflammation in hemodialysis (HD) patients.
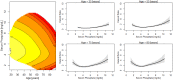
Methods: Adult HD patients (n = 245 853) treated in Fresenius Medical Care North America clinics from January 2010 to October 2018 were enrolled. Baseline was defined as Months 4-6 on dialysis, with the subsequent 12 months as the follow-up period. Univariate and multivariate Cox proportional hazard models with spline terms were applied to study the nonlinear relationships between serum phosphate levels and mortality. The interactions of phosphate levels with albumin, creatinine, normalized protein catabolic rate (nPCR) and neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio (NLR) were assessed with smoothing spline analysis of variance Cox proportional hazard models.
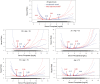
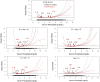
Results: Older patients tended to have lower levels of serum phosphate, albumin, creatinine and nPCR. Additionally, both low (<4.0 mg/dL) and high (>5.5 mg/dL) phosphate levels were associated with higher risk of mortality across all age strata. The U-shaped relationships between phosphate levels and outcome persisted even for patients with low or high levels of serum albumin, creatinine, nPCR and NLR, respectively.
Conclusion: The consistent U-shaped relationships between serum phosphate and mortality across age strata and levels of inflammatory and nutritional status should prompt the search for underlying causes and potentially nutritional intervention in clinical practice.
Keywords: hyperphosphatemia; hypophosphatemia; inflammation; malnutrition; protein–energy wasting.
© The Author(s) 2019. Published by Oxford University Press on behalf of ERA-EDTA.
Figures


References
-
- National Kidney Foundation. KDOQI US commentary on the 2017 KDIGO clinical practice guideline update for the diagnosis, evaluation, prevention, and treatment of chronic kidney disease-mineral and bone disorder (CKD-MBD). Am J Kidney Dis 2017; 70: 737–751 - PubMed
-
- Isakova T, Nickolas TL, Denburg M. et al. KDOQI US Commentary on the 2017 KDIGO Clinical Practice Guideline Update for the Diagnosis, Evaluation, Prevention, and Treatment of Chronic Kidney Disease-Mineral and Bone Disorder (CKD-MBD). Am J Kidney Dis 2017; 70: 737–751 - PubMed
-
- Block GA, Hulbert-Shearon TE, Levin NW. et al. Association of serum phosphorus and calcium x phosphate product with mortality risk in chronic hemodialysis patients: a national study. Am J Kidney Dis 1998; 31: 607–617 - PubMed
-
- Fernandez-Martin JL, Dusso A, Martinez-Camblor P. et al. Serum phosphate optimal timing and range associated with patients survival in haemodialysis: the COSMOS study. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2019; 34: 673–681 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

