Repeat and Relapsing Peritonitis Microbiological Trends and Outcomes: A 21-Year Single-Center Experience
- PMID: 33564478
- PMCID: PMC7867458
- DOI: 10.1155/2021/6662488
Repeat and Relapsing Peritonitis Microbiological Trends and Outcomes: A 21-Year Single-Center Experience
Abstract
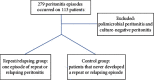
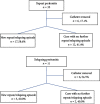
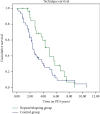
Peritonitis is a major peritoneal dialysis complication. Despite a high cure rate, relapsing and repeat peritonitis is associated with Tenckhoff catheter biofilm and multiple episodes of peritoneal damage. In relapsing peritonitis, prompt catheter removal is mandatory; otherwise, in repeat peritonitis, there is not a clear indication for catheter removal. It is questionable if the approach to removal should be different. There are few recent data on repeat and relapsing peritonitis microbiology and clinical outcomes since most studies are from the past decade. This study evaluates the microbiology, clinical outcomes, and impact of relapsing and repeat peritonitis on technique survival and the impact of catheter removal in development of further peritonitis episodes by the same microorganism. We developed a single-center retrospective study from 1998 to 2019 that compared repeat and relapsing peritonitis with a control group in terms of causative microorganisms, cure rate, catheter removal, and permanent and temporary transfer to hemodialysis. We also compared repeat and relapsing peritonitis clinical outcomes when Tenckhoff catheter was not removed. Comparing to the control group, the repeat/relapsing group had a higher cure rate (80.4% versus 74.5%, p=0.01) and lower rate of hospitalization (10.9% versus 27.7%, p=0.01). Technique survival was superior in the repeat/relapsing group (log rank = 4.5, p=0.03). Gram-positive peritonitis was more common in the repeat/relapsing group especially Streptococci viridans (43.5% versus 21.3%, p=0.01) and Gram-negatives in the control group (26.6% vs 9.0%, p=0.02). When the Tenckhoff catheter was not removed after a repeat episode, 58.6% developed a new repeat/relapsing episode versus 60.0% in the relapsing group. Although repeat and relapsing peritonitis have a higher cure rate, it leads to further episodes of peritonitis and consequent morbidity. When Tenckhoff catheter was not removed, the probability of another peritonitis episode by the same microorganism is similar in repeat and relapsing peritonitis.
Copyright © 2021 Marina Reis et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Repeat peritonitis in peritoneal dialysis: retrospective review of 181 consecutive cases.Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011 Apr;6(4):827-33. doi: 10.2215/CJN.05370610. Epub 2010 Dec 23. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2011. PMID: 21183587 Free PMC article.
-
Viridans streptococci in peritoneal dialysis peritonitis: clinical courses and long-term outcomes.Perit Dial Int. 2015 May-Jun;35(3):333-41. doi: 10.3747/pdi.2013.00108. Epub 2014 Feb 4. Perit Dial Int. 2015. PMID: 24497584 Free PMC article.
-
Clinical course of peritonitis due to Pseudomonas species complicating peritoneal dialysis: a review of 104 cases.Kidney Int. 2001 Jun;59(6):2309-15. doi: 10.1046/j.1523-1755.2001.00748.x. Kidney Int. 2001. PMID: 11380835
-
Rothia dentocariosa repeat and relapsing peritoneal dialysis-related peritonitis: a case report and literature review.Ren Fail. 2012;34(6):804-6. doi: 10.3109/0886022X.2012.678208. Epub 2012 Apr 17. Ren Fail. 2012. PMID: 22506572 Review.
-
The clinical course of culture-negative peritonitis complicating peritoneal dialysis.Am J Kidney Dis. 2003 Sep;42(3):567-74. doi: 10.1016/s0272-6386(03)00790-x. Am J Kidney Dis. 2003. PMID: 12955686 Review.
Cited by
-
Persistent peritonitis in peritoneal dialysis: a comphrenesive review of recurrent, relapsing, refractory, and repeat peritonitis.Int Urol Nephrol. 2024 Feb;56(2):583-595. doi: 10.1007/s11255-023-03731-w. Epub 2023 Aug 10. Int Urol Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 37563501 Review.
-
Prevalence, microbiology, and outcome of peritonitis in peritoneal dialysis patients in vietnam: a multicenter study.BMC Nephrol. 2025 Mar 11;26(1):134. doi: 10.1186/s12882-025-04061-y. BMC Nephrol. 2025. PMID: 40069647 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Finkelstein E. S., Jekel J., Troidle L., Gorban-Brennan N., Finkelstein F. O., Bia F. J. Patterns of infection in patients maintained on long-term peritoneal dialysis therapy with multiple episodes of peritonitis. American Journal of Kidney Diseases. 2002;39(6):1278–1286. doi: 10.1053/ajkd.2002.33403. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous