Alarming Eosinophilia From Dobutamine Infusion
- PMID: 33564531
- PMCID: PMC7863021
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.12530
Alarming Eosinophilia From Dobutamine Infusion
Abstract
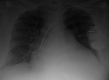
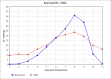
A 49-year-old male with a history of nonischemic heart failure with reduced ejection fraction, hypertension, diabetes was admitted for cardiogenic shock. Treatment started with a high dose of dobutamine infusion. While the patient's volume status improved, his clinical status declined as he became febrile and hypotensive. He was found to have severe dobutamine-induced eosinophilia, corrected only upon dobutamine cessation and steroid administration. A comprehensive investigation ruled out other potential etiologies. Peripheral eosinophilia is a rare adverse effect associated with dobutamine, leading to a significant deterioration in already decompensated patients.
Keywords: cardiogenic shock; critical care cardiology; dobutamine; drug-induced eosinophilia; eosinophila; heart failure; hyper-eosinophilia syndrome.
Copyright © 2021, Maaliki et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Blood eosinophilia: a new paradigm in disease classification, diagnosis, and treatment. Tefferi A. Mayo Clin Proc. 2005;80:75–83. - PubMed
-
- Hypereosinophilia with rash to dobutamine infusion; sulfite hypersensitivity diagnosed by in vitro stimulation assays. Kang SY, Lee JW, Park DE, et al. Allergol Int. 2016;65:477–480. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources