Prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)-targeted photodynamic therapy enhances the delivery of PSMA-targeted magnetic nanoparticles to PSMA-expressing prostate tumors
- PMID: 33564617
- PMCID: PMC7868004
- DOI: 10.7150/ntno.52361
Prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA)-targeted photodynamic therapy enhances the delivery of PSMA-targeted magnetic nanoparticles to PSMA-expressing prostate tumors
Abstract
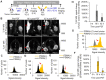
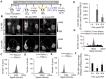
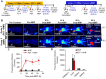
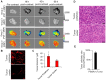
Enhanced vascular permeability in tumors plays an essential role in nanoparticle delivery. Prostate-specific membrane antigen (PSMA) is overexpressed on the epithelium of aggressive prostate cancers (PCs). Here, we evaluated the feasibility of increasing the delivery of PSMA-targeted magnetic nanoparticles (MNPs) to tumors by enhancing vascular permeability in PSMA(+) PC tumors with PSMA-targeted photodynamic therapy (PDT). Method: PSMA(+) PC3 PIP tumor-bearing mice were given a low-molecular-weight PSMA-targeted photosensitizer and treated with fluorescence image-guided PDT, 4 h after. The mice were then given a PSMA-targeted MNP immediately after PDT and monitored with fluorescence imaging and T2-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (T2-W MRI) 18 h, 42 h, and 66 h after MNP administration. Untreated PSMA(+) PC3 PIP tumor-bearing mice were used as negative controls. Results: An 8-fold increase in the delivery of the PSMA-targeted MNPs was detected using T2-W MRI in the pretreated tumors 42 h after PDT, compared to untreated tumors. Additionally, T2-W MRIs revealed enhanced peripheral intra-tumoral delivery of the PSMA-targeted MNPs. That finding is in keeping with two-photon microscopy, which revealed higher vascular densities at the tumor periphery. Conclusion: These results suggest that PSMA-targeted PDT enhances the delivery of PSMA-targeted MNPs to PSMA(+) tumors by enhancing the vascular permeability of the tumors.
Keywords: enhanced permeability and retention (EPR) effect; magnetic nanoparticle delivery; magnetic resonance imaging (MRI); photodynamic therapy (PDT); prostate cancer.
© The author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
Competing Interests: The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Figures





References
-
- Siegel RL, Miller KD, Jemal A. Cancer statistics, 2017. CA Cancer J Clin. 2017;67:7–30. - PubMed
-
- Zerbib M, Zelefsky MJ, Higano CS, Carroll PR. Conventional treatments of localized prostate cancer. Urology. 2008;72:S25–S35. - PubMed
-
- Ouzzane A, Betrouni N, Valerio M, Rastinehad A, Colin P, Ploussard G. Focal therapy as primary treatment for localized prostate cancer: definition, needs and future. Future Oncol. 2017;13:727–41. - PubMed
-
- Marberger M, Carroll PR, Zelefsky MJ, Coleman JA, Hricak H, Scardino PT. et al. New treatments for localized prostate cancer. Urology. 2008;72:S36–S43. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

