Evaluation of Oral Nutritional Supplementation in the Management of Frailty among the Elderly at Facilities of Community Care for the Elderly
- PMID: 33564650
- PMCID: PMC7850817
- DOI: 10.7762/cnr.2021.10.1.24
Evaluation of Oral Nutritional Supplementation in the Management of Frailty among the Elderly at Facilities of Community Care for the Elderly
Abstract
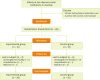
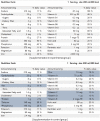
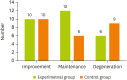
Adequate nutritional intake in elderly individuals improves frailty. Elderly individuals may exhibit improvements in frailty with the use of community care facilities. Therefore, this study evaluated the effects of nutritional intervention in elderly subjects at community care facilities receiving oral nutritional supplements (ONSs) and determined their nutritional status. Sixty-two elderly individuals using community care facilities were divided into the experimental group (EG) (before [n = 31]/after [n = 28]) and control group (CG) (before [n = 31]/after [n = 25]). Subjects in both groups were treated with ONSs (200 mL/200 kcal) for 90 days. However, those in the EG received the product with increased protein; vitamins A, C, D, and E; phosphorus; calcium; and zinc. The data collected included anthropometric data, dietary assessment findings, frailty status (Korean version of the Fatigue, Resistance, Ambulation, Illnesses, and Loss of weight questionnaire), and nutritional status (Mini Nutritional Assessment, MNA). The changes in the two groups were analyzed using the Mann-Whitney U Wilcoxon signed-rank test. Nutritional intervention increased the weight, body mass index, and lean body mass in the EG (p < 0.05). Protein, calcium, and iron levels increased only in the EG (p < 0.05). The MNA score increased and sum of frailty indicators improved in the EG, and the increase in the MNA score in the EG was greater than that in the CG. This study verified the improved anthropometric data and dietary intake in the EG. Thus, the higher number of pre-frailty elderly individuals at facilities of community care indicates the need for adequate nutritional supplementation for frailty management.
Keywords: Frailty; Nutritional status; Nutritional support; Randomized controlled trial.
Copyright © 2021. The Korean Society of Clinical Nutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Statistics Korea. Available from http://kostat.go.kr/portal/korea/index.action.
-
- Hyun EY, Oh JJ. Malnutritional status and it's related factors of demented elderly in long-term care facilities. J Korea Contents Assoc. 2017;17:426–436.
-
- Fried LP, Tangen CM, Walston J, Newman AB, Hirsch C, Gottdiener J, Seeman T, Tracy R, Kop WJ, Burke G, McBurnie MA Cardiovascular Health Study Collaborative Research Group. Frailty in older adults: evidence for a phenotype. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci. 2001;56:M146–56. - PubMed
-
- Won CW. Evaluation and management of frailty. J Korean Med Assoc. 2017;60:314–320.
-
- Walston J, Hadley EC, Ferrucci L, Guralnik JM, Newman AB, Studenski SA, Ershler WB, Harris T, Fried LP. Research agenda for frailty in older adults: toward a better understanding of physiology and etiology: summary from the American Geriatrics Society/National Institute on Aging Research Conference on Frailty in Older Adults. J Am Geriatr Soc. 2006;54:991–1001. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

