Probiotic Yogurt Fortified with Vitamin D Can Improve Glycemic Status in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Patients: a Randomized Clinical Trial
- PMID: 33564651
- PMCID: PMC7850818
- DOI: 10.7762/cnr.2021.10.1.36
Probiotic Yogurt Fortified with Vitamin D Can Improve Glycemic Status in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Patients: a Randomized Clinical Trial
Abstract
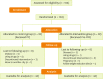
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a significant public health problem globally and the most notable chronic liver disease in Asian countries. Various dietary supplements have been assessed as potential methods to alleviate the metabolic damages related to NAFLD, but the results of these works have been equivocal. This study aimed to evaluate the effects of probiotic yogurt fortified with vitamin D (Pro-YFD) on glycemic and anthropometric indices in patients with NAFLD. One hundred and four NAFLD patients of both sexes were randomly allocated to 2 groups: group A (Pro-YFD) and group B (unfortified yogurt). The intervention period was 3 months. Fasting blood samples were obtained for measuring fasting blood sugar (FBS) and insulin level. Food intake was measured using a validated food frequency questionnaire. Body composition was estimated by bio-impedance. Eighty-eight patients completed the study. The mean serum level of 25(OH)D3 was elevated significantly (p < 0.001), while insulin level decreased significantly (p < 0.003) in group A at the end of the study. FBS levels showed no significant differences between the groups at the end of the trial. Also, there were no significant changes in diet caloric intake, physical activity, or anthropometric indices in the 2 groups during the interventions. Pro-YFD in the diets of patients with NAFLD may attenuate insulin resistance and improve serum level of 25(OH)D3.
Keywords: Glycemic index; Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease; Vitamin D; Yogurt.
Copyright © 2021. The Korean Society of Clinical Nutrition.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of Interest: The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Tiniakos DG, Vos MB, Brunt EM. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: pathology and pathogenesis. Annu Rev Pathol. 2010;5:145–171. - PubMed
-
- Pasdar Y, Moradi S, Moludi J, Darbandi M, Niazi P, Nachvak SM, Abdollahzad H. Risk of metabolic syndrome in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease patients. Med J Nutrition Metab. 2019;12:1–11.
-
- Farrell GC, Larter CZ. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: from steatosis to cirrhosis. Hepatology. 2006;43:S99–112. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

