This is a preprint.
Development of a highly sensitive bioanalytical assay for the quantification of favipiravir
- PMID: 33564761
- PMCID: PMC7872349
- DOI: 10.1101/2021.02.03.429628
Development of a highly sensitive bioanalytical assay for the quantification of favipiravir
Abstract
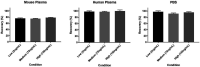
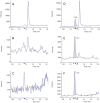
Favipiravir (FAV; T-705) has been approved for use as an anti-influenza therapeutic and has reports against a wide range of viruses (e.g., Ebola virus, rabies and norovirus). Most recently FAV has been reported to demonstrate activity against SARS-CoV-2. Repurposing opportunities have been intensively studied with only limited success to date. If successful, repurposing will allow interventions to become more rapidly available than development of new chemical entities. Pre-clinical and clinical investigations of FAV require robust, reproducible and sensitive bioanalytical assay. Here, a liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry assay is presented which was linear from 0.78-200 ng/mL Accuracy and precision ranged between 89% and 110%, 101% and 106%, respectively. The presented assay here has applications in both pre-clinical and clinical research and may be used to facilitate further investigations into the application of FAV against SARS-CoV-2.
Keywords: COVID-19; Favipiravir; LC-MS/MS; SARS-CoV-2; plasma.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest statement AO and SR have received research funding from AstraZeneca and ViiV and consultancies from Gilead; AO has additionally received funding from Merck and Janssen and consultancies from ViiV and Merck not related to the current paper. No other conflicts are declared by the authors.
Figures

References
-
- Delang L., Abdelnabi R., and Neyts J., Favipiravir as a potential countermeasure against neglected and emerging RNA viruses. Antiviral research, 2018. 153: p. 85–94. - PubMed
-
- Wang G., et al., Synthesis and anti-influenza activity of pyridine, pyridazine, and pyrimidine C-nucleosides as favipiravir (T-705) analogues. Journal of medicinal chemistry, 2016. 59(10): p. 4611–4624. - PubMed
-
- Oestereich L., et al., Successful treatment of advanced Ebola virus infection with T-705 (favipiravir) in a small animal model. Antiviral research, 2014. 105: p. 17–21. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
