This is a preprint.
A Quantitative Evaluation of COVID-19 Epidemiological Models
- PMID: 33564783
- PMCID: PMC7872378
- DOI: 10.1101/2021.02.06.21251276
A Quantitative Evaluation of COVID-19 Epidemiological Models
Abstract
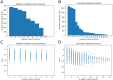
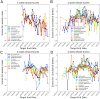
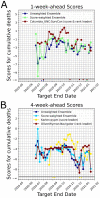
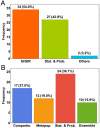
Quantifying how accurate epidemiological models of COVID-19 forecast the number of future cases and deaths can help frame how to incorporate mathematical models to inform public health decisions. Here we analyze and score the predictive ability of publicly available COVID-19 epidemiological models on the COVID-19 Forecast Hub. Our score uses the posted forecast cumulative distributions to compute the log-likelihood for held-out COVID-19 positive cases and deaths. Scores are updated continuously as new data become available, and model performance is tracked over time. We use model scores to construct ensemble models based on past performance. Our publicly available quantitative framework may aid in improving modeling frameworks, and assist policy makers in selecting modeling paradigms to balance the delicate trade-offs between the economy and public health.
Keywords: COVID-19; Epidemiology; Forecasting; Modeling; Scoring.
Figures


References
-
- Shea Katriona, Borchering Rebecca K, Probert William JM, Howerton Emily, Bogich Tiffany L, Li Shouli, van Panhuis Willem G, Viboud Cecile, Aguás Ricardo, Belov Artur, et al. Covid-19 reopening strategies at the county level in the face of uncertainty: Multiple models for outbreak decision support. medRxiv, 2020. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Press William H and Levin Richard C. Modeling, post covid-19, 2020. - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control, Prevention, et al. Flusight: Flu forecasting, 2019.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous
