In search of the RNA world on Mars
- PMID: 33565260
- PMCID: PMC8248371
- DOI: 10.1111/gbi.12433
In search of the RNA world on Mars
Abstract
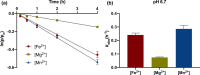
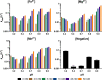
Advances in origins of life research and prebiotic chemistry suggest that life as we know it may have emerged from an earlier RNA World. However, it has been difficult to reconcile the conditions used in laboratory experiments with real-world geochemical environments that may have existed on the early Earth and hosted the origin(s) of life. This challenge is due to geologic resurfacing and recycling that have erased the overwhelming majority of the Earth's prebiotic history. We therefore propose that Mars, a planet frozen in time, comprised of many surfaces that have remained relatively unchanged since their formation > 4 Gya, is the best alternative to search for environments consistent with geochemical requirements imposed by the RNA world. In this study, we synthesize in situ and orbital observations of Mars and modeling of its early atmosphere into solutions containing a range of pHs and concentrations of prebiotically relevant metals (Fe2+ , Mg2+ , and Mn2+ ) spanning various candidate aqueous environments. We then experimentally determine RNA degradation kinetics due to metal-catalyzed hydrolysis (cleavage) and evaluate whether early Mars could have been permissive toward the accumulation of long-lived RNA polymers. Our results indicate that a Mg2+ -rich basalt sourcing metals to a slightly acidic (pH 5.4) environment mediates the slowest rates of RNA cleavage, though geologic evidence and basalt weathering models suggest aquifers on Mars would be near neutral (pH ~ 7). Moreover, the early onset of oxidizing conditions on Mars has major consequences regarding the availability of oxygen-sensitive metals (i.e., Fe2+ and Mn2+ ) due to increased RNA degradation rates and precipitation. Overall, (a) low pH decreases RNA cleavage at high metal concentrations; (b) acidic to neutral pH environments with Fe2+ or Mn2+ cleave more RNA than Mg2+ ; and (c) alkaline environments with Mg2+ dramatically cleaves more RNA while precipitates were observed for Fe2+ and Mn2+ .
Keywords: Mars; RNA world; origins of life.
© 2021 The Authors. Geobiology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Resolving the History of Life on Earth by Seeking Life As We Know It on Mars.Astrobiology. 2022 Jul;22(7):880-888. doi: 10.1089/ast.2021.0043. Epub 2022 Apr 25. Astrobiology. 2022. PMID: 35467949 Free PMC article.
-
Boron enrichment in martian clay.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 6;8(6):e64624. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0064624. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23762242 Free PMC article.
-
Paleo-Rock-Hosted Life on Earth and the Search on Mars: A Review and Strategy for Exploration.Astrobiology. 2019 Oct;19(10):1230-1262. doi: 10.1089/ast.2018.1960. Epub 2019 Jun 25. Astrobiology. 2019. PMID: 31237436 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characterizing the Mineral Assemblages of Hot Spring Environments and Applications to Mars Orbital Data.Astrobiology. 2020 Apr;20(4):453-474. doi: 10.1089/ast.2018.2003. Epub 2019 Sep 23. Astrobiology. 2020. PMID: 31545076
-
Could the early environment of Mars have supported the development of life?Earth Space. 1990 Jan;2(5):10-2. Earth Space. 1990. PMID: 11538711 Review.
Cited by
-
Groundwater-Driven Evolution of Prebiotic Alkaline Lake Environments.Life (Basel). 2024 Dec 7;14(12):1624. doi: 10.3390/life14121624. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39768332 Free PMC article.
-
Probing the Limits of Reactant Concentration and Volume in Primitive Polyphenyllactate Synthesis and Microdroplet Assembly Processes.ACS Bio Med Chem Au. 2025 Jan 9;5(1):131-142. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomedchemau.4c00082. eCollection 2025 Feb 19. ACS Bio Med Chem Au. 2025. PMID: 39990942 Free PMC article.
-
UV Transmission in Natural Waters on Prebiotic Earth.Astrobiology. 2022 Mar;22(3):242-262. doi: 10.1089/ast.2020.2422. Epub 2021 Dec 16. Astrobiology. 2022. PMID: 34939825 Free PMC article.
-
Origin of Life on Mars: Suitability and Opportunities.Life (Basel). 2021 Jun 9;11(6):539. doi: 10.3390/life11060539. Life (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34207658 Free PMC article.
-
Resolving the History of Life on Earth by Seeking Life As We Know It on Mars.Astrobiology. 2022 Jul;22(7):880-888. doi: 10.1089/ast.2021.0043. Epub 2022 Apr 25. Astrobiology. 2022. PMID: 35467949 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adcock, C. T. , Hausrath, E. M. , & Forster, P. M. (2013). Readily available phosphate from minerals in early aqueous environments on Mars. Nature Geoscience, 6, 824–827. 10.1038/ngeo1923 - DOI
-
- Allwood, A. C. , Grotzinger, J. P. , Knoll, A. H. , Burch, I. W. , Anderson, M. S. , Coleman, M. L. , & Kanik, I. (2009). Controls on development and diversity of Early Archean stromatolites. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 106, 9548–9555. 10.1073/pnas.0903323106 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

