Correlation of hepcidin and serum ferritin levels in thalassemia patients at Chiang Mai University Hospital
- PMID: 33565577
- PMCID: PMC7886874
- DOI: 10.1042/BSR20203352
Correlation of hepcidin and serum ferritin levels in thalassemia patients at Chiang Mai University Hospital
Abstract
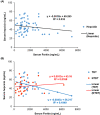
Hepcidin is a key iron-regulatory hormone, the production of which is controlled by iron stores, inflammation, hypoxia and erythropoiesis. The regulation of iron by hepcidin is of clinical importance in thalassemia patients in which anemia occurs along with iron overload. The present study aimed to evaluate the correlation between serum hepcidin and ferritin levels in thalassemia patients. This cross-sectional study investigated 64 patients with thalassemia; 16 β-thalassemia major (BTM), 31 β-thalassemia/hemoglobin (Hb) E (BE), and 17 Hb H + AE Bart's disease (Hb H + AE Bart's). The levels of serum hepcidin and ferritin, and Hb of the three groups were measured. The median values of serum ferritin and Hb were significantly different among the three groups, whereas serum hepcidin values were not observed to be significantly different. The correlation of the serum hepcidin and ferritin levels was not statistically significant in any of the three groups of thalassemia patients with BTM, BE, or Hb H + AE Bart's (r = -0.141, 0.065 and -0.016, respectively). In conclusion, no statistically significant correlations were observed between serum hepcidin with any variables including serum ferritin, Hb, age, labile plasma iron (LPI), and number of blood transfusion units among the three groups of thalassemia patients. Likely, the regulation of hepcidin in thalassemia patients is affected more by erythropoietic activity than iron storage.
Keywords: Hb H disease; ferritin; hepcidin; β-thalassemia major; β-thalassemia/Hb E.
© 2021 The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that there are no competing interests associated with the manuscript.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Imbalance of erythropoiesis and iron metabolism in patients with thalassemia.Int J Med Sci. 2019 Jan 1;16(2):302-310. doi: 10.7150/ijms.27829. eCollection 2019. Int J Med Sci. 2019. PMID: 30745811 Free PMC article.
-
Serum Hepcidin as a Diagnostic Marker of Severe Iron Overload in Beta-thalassemia Major.Indian J Pediatr. 2017 Oct;84(10):745-750. doi: 10.1007/s12098-017-2375-4. Epub 2017 Jun 10. Indian J Pediatr. 2017. PMID: 28600663
-
Iron Status in Newly Diagnosed β-Thalassemia Major: High Rate of Iron Status due to Erythropoiesis Drive.Biomed Res Int. 2021 Apr 16;2021:5560319. doi: 10.1155/2021/5560319. eCollection 2021. Biomed Res Int. 2021. PMID: 33954177 Free PMC article.
-
Impact of Inflammation on Ferritin, Hepcidin and the Management of Iron Deficiency Anemia in Chronic Kidney Disease.Nutrients. 2018 Aug 27;10(9):1173. doi: 10.3390/nu10091173. Nutrients. 2018. PMID: 30150549 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activation of STAT and SMAD Signaling Induces Hepcidin Re-Expression as a Therapeutic Target for β-Thalassemia Patients.Biomedicines. 2022 Jan 17;10(1):189. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10010189. Biomedicines. 2022. PMID: 35052868 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Correlation Between Serum Ferritin and Hepcidin Levels in Chronic Hepatitis C Patients.Cureus. 2021 Aug 27;13(8):e17484. doi: 10.7759/cureus.17484. eCollection 2021 Aug. Cureus. 2021. PMID: 34603871 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Splenectomy on Natural Killer Cell Levels in β-Thalassemia Major Patients.J Clin Lab Anal. 2024 May;38(9):e25046. doi: 10.1002/jcla.25046. J Clin Lab Anal. 2024. PMID: 38814004 Free PMC article.
-
The effect of blood transfusion on serum hepcidin levels in chronically transfused patients of β-thalassemia major: An observational study in a tertiary care centre in Western Maharashtra.Asian J Transfus Sci. 2024 Jan-Jun;18(1):73-78. doi: 10.4103/ajts.ajts_160_22. Epub 2023 Aug 2. Asian J Transfus Sci. 2024. PMID: 39036689 Free PMC article.
-
Severe hyperferremia and hyperferritinemia in a dog with precursor-directed immune-mediated anemia.Vet Clin Pathol. 2022 Dec;51(4):491-494. doi: 10.1111/vcp.13130. Epub 2022 May 16. Vet Clin Pathol. 2022. PMID: 35578377 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiac injury caused by iron overload in thalassemia.Front Pediatr. 2025 Jan 27;13:1514722. doi: 10.3389/fped.2025.1514722. eCollection 2025. Front Pediatr. 2025. PMID: 39931654 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fucharoen S. and Winichagoon P. (1992) Thalassemia in SouthEast Asia: problems and strategy for prevention and control. Southeast Asian J. Trop. Med. Public Health 23, 647–655 - PubMed
-
- Forget B.G. (2001) Molecular mechanisms of b thalassemia. In Disorders of Hemoglobin(Steinberg M.H., Forget B.G., Higgs D.R. and Nagel R.L., eds), pp. 252–276, Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, U.K.
-
- Gardenghi S., Marongiu M.F., Ramos P., Guy E., Breda L., Chadburn A.et al. . (2007) Ineffective erythropoiesis in beta-thalassemia is characterized by increased iron absorption mediated by down-regulation of hepcidin and up-regulation of ferroportin. Blood 109, 5027–5035 10.1182/blood-2006-09-048868 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

