Cell-Based Identification of New IDO1 Modulator Chemotypes
- PMID: 33565680
- PMCID: PMC8252559
- DOI: 10.1002/anie.202016004
Cell-Based Identification of New IDO1 Modulator Chemotypes
Abstract
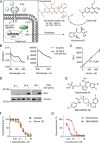
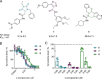
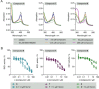
The immunoregulatory enzyme indoleamine-2,3-dioxygenase (IDO1) strengthens cancer immune escape, and inhibition of IDO1 by means of new chemotypes and mechanisms of action is considered a promising opportunity for IDO1 inhibitor discovery. IDO1 is a cofactor-binding, redox-sensitive protein, which calls for monitoring of IDO1 activity in its native cellular environment. We developed a new, robust fluorescence-based assay amenable to high throughput, which detects kynurenine in cells. Screening of a ca. 150 000-member compound library discovered unprecedented, potent IDO1 modulators with different mechanisms of action, including direct IDO1 inhibitors, regulators of IDO1 expression, and inhibitors of heme synthesis. Three IDO1-modulator chemotypes were identified that bind to apo-IDO1 and compete with the heme cofactor. Our new cell-based technology opens up novel opportunities for medicinal chemistry programs in immuno-oncology.
Keywords: cancer; fluorescence; heme proteins; high throughput screening; immunology.
© 2021 The Authors. Angewandte Chemie International Edition published by Wiley-VCH GmbH.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

References
-
- Adams J. L., Smothers J., Srinivasan R., Hoos A., Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery 2015, 14, 603–622. - PubMed
-
- None
-
- Godin-Ethier J., Pelletier S., Hanafi L. A., Gannon P. O., Forget M. A., Routy J. P., Boulassel M. R., Krzemien U., Tanguay S., Lattouf J. B., Arbour N., Lapointe R., J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 7752–7760; - PubMed
-
- Théate I., van Baren N., Pilotte L., Moulin P., Larrieu P., Renauld J. C., Hervé C., Gutierrez-Roelens I., Marbaix E., Sempoux C., Van den Eynde B. J., Cancer Immunol. Res. 2015, 3, 161–172. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

