Clinical use of donation after circulatory death pancreas for islet transplantation
- PMID: 33565712
- PMCID: PMC8518956
- DOI: 10.1111/ajt.16533
Clinical use of donation after circulatory death pancreas for islet transplantation
Abstract
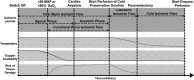
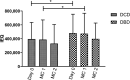
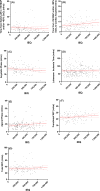
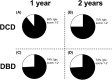
Due to a shortage of donation after brain death (DBD) organs, donation after circulatory death (DCD) is increasingly performed. In the field of islet transplantation, there is uncertainty regarding the suitability of DCD pancreas in terms of islet yield and function after islet isolation. The aim of this study was to investigate the potential use of DCD pancreas for islet transplantation. Islet isolation procedures from 126 category 3 DCD and 258 DBD pancreas were performed in a 9-year period. Islet yield after isolation was significantly lower for DCD compared to DBD pancreas (395 515 islet equivalents [IEQ] and 480 017 IEQ, respectively; p = .003). The decrease in IEQ during 2 days of culture was not different between the two groups. Warm ischemia time was not related to DCD islet yield. In vitro insulin secretion after a glucose challenge was similar between DCD and DBD islets. After islet transplantation, DCD islet graft recipients had similar graft function (AUC C-peptide) during mixed meal tolerance tests and Igls score compared to DBD graft recipients. In conclusion, DCD islets can be considered for clinical islet transplantation.
Keywords: basic (laboratory) research/science; clinical research/practice; diabetes: type 1; donors and donation: donation after circulatory death (DCD); islet isolation; islet transplantation; islets of Langerhans; organ acceptance; regenerative medicine.
© 2021 The Authors. American Journal of Transplantation published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors of this manuscript have no conflicts of interest to disclose as described by the
Figures


Comment in
-
Warm ischemia time influences human islet cell isolation yield when assessed as beta cell number but not as islet equivalent number.Am J Transplant. 2021 Nov;21(11):3814-3815. doi: 10.1111/ajt.16691. Epub 2021 Jun 2. Am J Transplant. 2021. PMID: 34008319 No abstract available.
References
-
- Shapiro AMJ, Lakey JRT, Ryan EA, et al. Islet transplantation in seven patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus using a glucocorticoid‐free immunosuppressive regimen. N Engl J Med. 2000;343(4):230‐238. - PubMed
-
- Hering BJ, Ansite JD, Eckman PM, Parkey J, Hunter DW, Sutherland DER. Single‐donor, marginal‐dose islet transplantation in patients with type 1 diabetes. JAMA. 2005;293(7):830‐836. - PubMed
-
- Organ Procurement and Transplantation Network . Organ Donation and Transplantation Statistics. https://optn.transplant.hrsa.gov/. Published 2018. Accessed January 26, 2019.
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

