Par-3 family proteins in cell polarity & adhesion
- PMID: 33565714
- PMCID: PMC9290619
- DOI: 10.1111/febs.15754
Par-3 family proteins in cell polarity & adhesion
Abstract
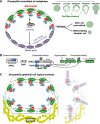
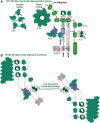
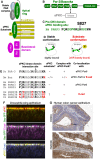
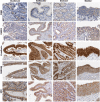
The Par-3/Baz family of polarity determinants is highly conserved across metazoans and includes C. elegans PAR-3, Drosophila Bazooka (Baz), human Par-3 (PARD3), and human Par-3-like (PARD3B). The C. elegans PAR-3 protein localises to the anterior pole of asymmetrically dividing zygotes with cell division cycle 42 (CDC42), atypical protein kinase C (aPKC), and PAR-6. The same C. elegans 'PAR complex' can also localise in an apical ring in epithelial cells. Drosophila Baz localises to the apical pole of asymmetrically dividing neuroblasts with Cdc42-aPKC-Par6, while in epithelial cells localises both in an apical ring with Cdc42-aPKC-Par6 and with E-cadherin at adherens junctions. These apical and junctional localisations have become separated in human PARD3, which is strictly apical in many epithelia, and human PARD3B, which is strictly junctional in many epithelia. We discuss the molecular basis for this fundamental difference in localisation, as well as the possible functions of Par-3/Baz family proteins as oligomeric clustering agents at the apical domain or at adherens junctions in epithelial stem cells. The evolution of Par-3 family proteins into distinct apical PARD3 and junctional PARD3B orthologs coincides with the emergence of stratified squamous epithelia in vertebrates, where PARD3B, but not PARD3, is strongly expressed in basal layer stem cells - which lack a typical apical domain. We speculate that PARD3B may contribute to clustering of E-cadherin, signalling from adherens junctions via Src family kinases or mitotic spindle orientation by adherens junctions in response to mechanical forces.
Keywords: E-cadherin; cell adhesion; epithelia; neuroblast; polarity; stem cell.
© 2021 The Authors. The FEBS Journal published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A Par-1-Par-3-Centrosome Cell Polarity Pathway and Its Tuning for Isotropic Cell Adhesion.Curr Biol. 2015 Oct 19;25(20):2701-8. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2015.08.063. Epub 2015 Oct 8. Curr Biol. 2015. PMID: 26455305
-
Antagonistic functions of Par-1 kinase and protein phosphatase 2A are required for localization of Bazooka and photoreceptor morphogenesis in Drosophila.Dev Biol. 2007 Jun 15;306(2):624-35. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2007.03.522. Epub 2007 Apr 1. Dev Biol. 2007. PMID: 17475233 Free PMC article.
-
Cdc42 acts downstream of Bazooka to regulate neuroblast polarity through Par-6 aPKC.J Cell Sci. 2007 Sep 15;120(Pt 18):3200-6. doi: 10.1242/jcs.014902. Epub 2007 Aug 28. J Cell Sci. 2007. PMID: 17726059 Free PMC article.
-
Intercellular junctions and cellular polarity: the PAR-aPKC complex, a conserved core cassette playing fundamental roles in cell polarity.Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001 Oct;13(5):641-8. doi: 10.1016/s0955-0674(00)00264-7. Curr Opin Cell Biol. 2001. PMID: 11544035 Review.
-
The interdependence of the Rho GTPases and apicobasal cell polarity.Small GTPases. 2014;5(2):10. doi: 10.4161/21541248.2014.973768. Small GTPases. 2014. PMID: 25469537 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Par3L, a polarity protein, promotes M1 macrophage polarization and aggravates atherosclerosis in mice via p65 and ERK activation.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024 Jan;45(1):112-124. doi: 10.1038/s41401-023-01161-z. Epub 2023 Sep 20. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024. PMID: 37731037 Free PMC article.
-
Locus coeruleus vulnerability to tau hyperphosphorylation in a rat model.Aging Cell. 2025 Mar;24(3):e14405. doi: 10.1111/acel.14405. Epub 2024 Nov 9. Aging Cell. 2025. PMID: 39520141 Free PMC article.
-
Loss of intermicrovillar adhesion factor CDHR2 impairs basolateral junctional complexes in transporting epithelia.Mol Biol Cell. 2024 Nov 1;35(11):br21. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E24-03-0113. Epub 2024 Sep 18. Mol Biol Cell. 2024. PMID: 39292922 Free PMC article.
-
E-cadherin acts as a positive regulator of the JAK-STAT signaling pathway during Drosophila oogenesis.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Aug 23;10:886312. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.886312. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36120588 Free PMC article.
-
Wings of Change: aPKC/FoxP-dependent plasticity in steering motor neurons underlies operant self-learning in Drosophila.F1000Res. 2024 Jun 11;13:116. doi: 10.12688/f1000research.146347.2. eCollection 2024. F1000Res. 2024. PMID: 38779314 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Martin‐Belmonte F & Perez‐Moreno M (2012) Epithelial cell polarity, stem cells and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 12, 23–38. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

