Lactate in contemporary biology: a phoenix risen
- PMID: 33566386
- PMCID: PMC9188361
- DOI: 10.1113/JP280955
Lactate in contemporary biology: a phoenix risen
Abstract
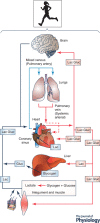
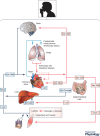
After a century, it's time to turn the page on understanding of lactate metabolism and appreciate that lactate shuttling is an important component of intermediary metabolism in vivo. Cell-cell and intracellular lactate shuttles fulfil purposes of energy substrate production and distribution, as well as cell signalling under fully aerobic conditions. Recognition of lactate shuttling came first in studies of physical exercise where the roles of driver (producer) and recipient (consumer) cells and tissues were obvious. Moreover, the presence of lactate shuttling as part of postprandial glucose disposal and satiety signalling has been recognized. Mitochondrial respiration creates the physiological sink for lactate disposal in vivo. Repeated lactate exposure from regular exercise results in adaptive processes such as mitochondrial biogenesis and other healthful circulatory and neurological characteristics such as improved physical work capacity, metabolic flexibility, learning, and memory. The importance of lactate and lactate shuttling in healthful living is further emphasized when lactate signalling and shuttling are dysregulated as occurs in particular illnesses and injuries. Like a phoenix, lactate has risen to major importance in 21st century biology.
Keywords: exercise; fibre type; gene adaptation; gluconeogenesis; glycogenolysis; indirect pathway; lactate shuttle; lactate signalling; microbiome; muscle; postabsorptive metabolism; postprandial metabolism; satiety.
© 2021 The Authors. The Journal of Physiology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of The Physiological Society.
Figures

Comment in
-
How high can the lactate phoenix rise?J Physiol. 2022 Jun;600(11):2813-2814. doi: 10.1113/JP283089. Epub 2022 May 10. J Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35538348 No abstract available.
-
Reply from George A. Brooks.J Physiol. 2022 Jun;600(11):2815. doi: 10.1113/JP283189. Epub 2022 May 10. J Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35538394 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Ahmed K, Tunaru S, Tang C, Muller M, Gille A, Sassmann A, Hanson J & Offermanns S (2010). An autocrine lactate loop mediates insulin‐dependent inhibition of lipolysis through GPR81. Cell Metab 11, 311–319. - PubMed
-
- Atlante A, de Bari L, Bobba A, Marra E & Passarella S (2007). Transport and metabolism of L‐lactate occur in mitochondria from cerebellar granule cells and are modified in cells undergoing low potassium dependent apoptosis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1767, 1285–1299. - PubMed
-
- Azevedo JL Jr, Linderman JK, Lehman SL & Brooks GA (1998). Training decreases muscle glycogen turnover during exercise. Eur J Appl Physiol Occup Physiol 78, 479–486. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

