A novel echocardiographic method for estimation of pulmonary artery wedge pressure and pulmonary vascular resistance
- PMID: 33566429
- PMCID: PMC8006655
- DOI: 10.1002/ehf2.13183
A novel echocardiographic method for estimation of pulmonary artery wedge pressure and pulmonary vascular resistance
Abstract
Aims: This study aimed to evaluate a novel echocardiographic algorithm for quantitative estimation of pulmonary artery wedge pressure (PAWP) and pulmonary vascular resistance (PVR) in patients with heart failure and pulmonary hypertension (PH) scheduled to right heart catheterization (RHC).
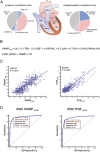
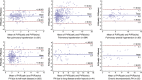
Methods and results: In this monocentric study, 795 consecutive patients (427 men; age 68.4 ± 12.1 years) undergoing echocardiography and RHC were evaluated. Multiple regression analysis was performed to identify echocardiographic predictors of PAWP and PVR measured by RHC in the derivation group (the first 200 patients). The diagnostic accuracy of the model was then tested in the validation group (the remaining 595 patients). PH was confirmed by RHC in 507 (63.8%) patients, with 192 (24.2%) cases of precapillary PH, 248 (31.2%) of postcapillary PH, and 67 (8.4%) of combined PH. At regression analysis, tricuspid regurgitation maximal velocity, mitral E/e' ratio, left ventricular ejection fraction, right ventricular fractional area change, inferior vena cava diameter, and left atrial volume index were included in the model (R = 0.8, P < 0.001). The model showed a high diagnostic accuracy in estimating elevated PAWP (area under the receiver operating characteristic curve = 0.97, 92% sensitivity, and 93% specificity, P < 0.001) and PVR (area under the receiver operating characteristic curve = 0.96, 89% sensitivity, and 92% specificity, P < 0.001), outperforming 2016 American Society of Echocardiography/European Association of Cardiovascular Imaging recommendations (P < 0.001) and Abbas' equation (P < 0.001). Bland-Altman analysis showed satisfactory limits of agreement between echocardiography and RHC for PAWP (bias 0.7, 95% confidence interval -7.3 to 8.7) and PVR (bias -0.1, 95% confidence interval -2.2 to 1.9 Wood units), without indeterminate cases.
Conclusions: A novel quantitative echocardiographic approach for the estimation of PAWP and PVR has high diagnostic accuracy in patients with heart failure and PH.
Keywords: Echocardiography; Pulmonary artery wedge pressure; Pulmonary hypertension; Pulmonary vascular resistance; Right heart catheterization.
© 2021 The Authors. ESC Heart Failure published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of European Society of Cardiology.
Conflict of interest statement
None declared.
Figures

References
-
- Galiè N, Humbert M, Vachiéry J‐L, Gibbs S, Lang I, Torbicki A, Simonneau G, Peacock A, Noordegraaf AV, Beghetti M, Ghofrani A, Sanchez MAG, Hansmann G, Klepetko W, Lancellotti P, Matucci M, McDonagh T, Pierard LA, Trindade PT, Zompatori M, Hoeper M, ESC Scientific Document Group . 2015 ESC/ERS guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur Heart J 2016; 37: 67–119. - PubMed
-
- Simonneau G, Gatzoulis MA, Adatia I, Celermajer D, Denton C, Ghofrani A, Gomez Sanchez MA, Krishna Kumar R, Landzberg M, Machado RF, Olschewski H, Robbins IM, Souza R. Updated clinical classification of pulmonary hypertension. J Am Coll Cardiol 2013; 62: D34–D41. - PubMed
-
- Ponikowski P, Voors AA, Anker SD, Bueno H, Cleland JGF, Coats AJS, Falk V, González‐Juanatey JR, Harjola V‐P, Jankowska EA, Jessup M, Linde C, Nihoyannopoulos P, Parissis JT, Pieske B, Riley JP, Rosano GMC, Ruilope LM, Ruschitzka F, Rutten FH, van der Meer P, Authors/Task Force Members . 2016 ESC guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic heart failure. Eur Heart J 2016; 37: 2129–2200. - PubMed
-
- Abbas AE, Franey LM, Marwick T, Maeder MT, Kaye DM, Vlahos AP, Serra W, al‐Azizi K, Schiller NB, Lester SJ. Noninvasive assessment of pulmonary vascular resistance by Doppler echocardiography. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 2013; 26: 1170–1177. - PubMed
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

