GDF-15 as a Biomarker in Cardiovascular Disease
- PMID: 33566936
- PMCID: PMC8159541
- DOI: 10.36660/abc.20200426
GDF-15 as a Biomarker in Cardiovascular Disease
Abstract
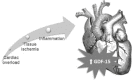
In the last years, several diagnostic and prognostic biomarkers have been studied in cardiovascular disease. Growth differentiation factor-15 (GDF-15), a cytokine belonging to the transforming growth factor- (TGF-) family, is highly up-regulated in stress and inflammatory conditions and has been correlated to myocardial injury and pressure cardiac overload in animal models. This new biomarker has been positively correlated with increased risk of cardiovascular events in population studies and shown an independent predictor of mortality in patients with coronary artery disease and heart failure. This review aimed to summarize the current evidence on the diagnostic and prognostic value of GDF-15 in different settings in cardiology.
Nos últimos anos, vários biomarcadores estão ganhando importância clínica na avaliação diagnóstica e prognóstica de pacientes com doenças cardiovasculares. O fator de crescimento e diferenciação celular-15 (GDF-15) é uma citocina induzida por estresse e inflamação, membro da família do TGF-, cuja produção no miocárdio foi demonstrada experimentalmente em resposta à injúria isquêmica ou sobrecarga cardíaca. Este novo marcador foi positivamente correlacionado com aumento do risco de eventos cardiovasculares em estudos populacionais e configurou-se preditor independente de mortalidade e prognóstico adverso em pacientes com doença arterial coronariana e insuficiência cardíaca. Este trabalho tem como objetivo revisar o valor diagnóstico e prognóstico do GDF-15 em diferentes cenários na cardiologia.
Conflict of interest statement
Potencial Conflito de Interesses
Declaro não haver conflito de interesses pertinentes.
Figures



References
-
- . Xu J, Kimball TR, Lorenz JN, Brown DA, Bauskin AR, Klevitsky R, et al. GDF15/MIC-1 functions as a protective and antihypertrophic factor released from the myocardium in association with SMAD protein activation. Circ Res. 2006;98(3):342–50. - PubMed
- Xu J, Kimball TR, Lorenz JN, Brown DA, Bauskin AR, Klevitsky R, et al. GDF15/MIC-1 functions as a protective and antihypertrophic factor released from the myocardium in association with SMAD protein activation. Circ Res . 2006;98(3):342–350. - PubMed
-
- . Kempf T, Eden M, Strelau J, Naguib M, Willenbockel C, Tongers J, et al. The transforming growth factor- superfamily member growth-differentiation factor-15 protects the heart from ischemia/reperfusion injury. Circ Res. 2006;98(3):351–60. - PubMed
- Kempf T, Eden M, Strelau J, Naguib M, Willenbockel C, Tongers J, et al. The transforming growth factor- superfamily member growth-differentiation factor-15 protects the heart from ischemia/reperfusion injury. Circ Res . 2006;98(3):351–360. - PubMed
-
- . Wang T, Liu J, McDonald C, Lupino K, Zhai X, Wilkins BJ, et al. GDF 15 is a heart-derived hormone that regulates body growth. EMBO Mol Med. 2017;9(8):1150–64. - PMC - PubMed
- Wang T, Liu J, McDonald C, Lupino K, Zhai X, Wilkins BJ, et al. GDF 15 is a heart-derived hormone that regulates body growth. EMBO Mol Med . 2017;9(8):1150–1164. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

