Position Statement on Fat Consumption and Cardiovascular Health - 2021
- PMID: 33566983
- PMCID: PMC8159504
- DOI: 10.36660/abc.20201340
Position Statement on Fat Consumption and Cardiovascular Health - 2021
Erratum in
-
Erratum.Arq Bras Cardiol. 2021 Apr;116(4):855. doi: 10.36660/abc.20210278. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2021. PMID: 33886741 Free PMC article. English, Portuguese.
Figures

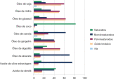
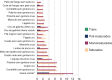
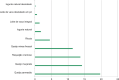


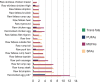
References
-
- . World Health Organization (WHO). Global Health Observatory. [Cited in 2019 Dec 12]. Available from: https://www.who.int/gho/ncd/mortality_morbidity/en/
-
- . Brasil. Ministério da Saúde. Vigitel Brasil 2018: vigilância de fatores de risco e proteção para doenças crônicas por inquérito telefônico: estimativas sobre frequência e distribuição sócio demográfica de fatores de risco e proteção para doenças crônicas nas capitais dos 26 estados brasileiros e no Distrito Federal em 2018. Brasília; 2019.
-
- . Page IH, Stareb FJ, Corcoran AC et al. Atherosclerosis and the fat content of the diet. J Am Med Assoc. 1957; 164(18):2048-51. - PubMed
-
- . The Facts on Fats. 50 years of American Heart Association - Dietary Fats Recomendations. American Heart Association; American Stroke Association. https://www.heart.org/-/media/files/healthy-living/company collaboration/inap/fats-white-paper-ucm_475005.pdf.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

