Natural genetic variation determines microglia heterogeneity in wild-derived mouse models of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 33567283
- PMCID: PMC7937391
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.108739
Natural genetic variation determines microglia heterogeneity in wild-derived mouse models of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
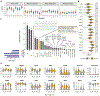
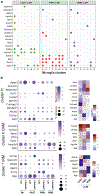
Genetic and genome-wide association studies suggest a central role for microglia in Alzheimer's disease (AD). However, single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) of microglia in mice, a key preclinical model, has shown mixed results regarding translatability to human studies. To address this, scRNA-seq of microglia from C57BL/6J (B6) and wild-derived strains (WSB/EiJ, CAST/EiJ, and PWK/PhJ) with and without APP/PS1 demonstrates that genetic diversity significantly alters features and dynamics of microglia in baseline neuroimmune functions and in response to amyloidosis. Results show significant variation in the abundance of microglial subtypes or states, including numbers of previously identified disease-associated and interferon-responding microglia, across the strains. For each subtype, significant differences in the expression of many genes are observed in wild-derived strains relative to B6, including 19 genes previously associated with human AD including Apoe, Trem2, and Sorl1. This resource is critical in the development of appropriately targeted therapeutics for AD and other neurological diseases.
Keywords: AD; APP/PS1; Alzheimer's disease; CAST/EiJ; DAM; IRM; PWK/PhJ; WSB/EiJ; disease-associated microglia; genetic diversity; interferon-responding microglia; microglia; wild-derived.
Copyright © 2021 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures





References
-
- Abdul-Sater AA, Saïd-Sadier N, Lam VM, Singh B, Pettengill MA, Soares F, Tattoli I, Lipinski S, Girardin SE, Rosenstiel P, and Ojcius DM (2010). Enhancement of reactive oxygen species production and chlamydial infection by the mitochondrial Nod-like family member NLRX1. J. Biol. Chem 285, 41637–41645. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Adriouch S, Dox C, Welge V, Seman M, Koch-Nolte F, and Haag F (2002). Cutting edge: a natural P451L mutation in the cytoplasmic domain impairs the function of the mouse P2X7 receptor. J. Immunol 169, 4108–4112. - PubMed
-
- Agora Consortium (2020). Agora. https://agora.ampadportal.org/genes.
-
- Angerer P, Haghverdi L, Buttner M, Theis FJ, Marr C, and Buettner F (2016). destiny: diffusion maps for large-scale single-cell data in R. Bioinformatics 32, 1241–1243. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

