Therapeutic promise of engineered nonsense suppressor tRNAs
- PMID: 33567469
- PMCID: PMC8244042
- DOI: 10.1002/wrna.1641
Therapeutic promise of engineered nonsense suppressor tRNAs
Abstract
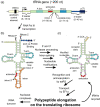
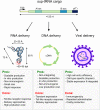
Nonsense mutations change an amino acid codon to a premature termination codon (PTC) generally through a single-nucleotide substitution. The generation of a PTC results in a defective truncated protein and often in severe forms of disease. Because of the exceedingly high prevalence of nonsense-associated diseases and a unifying mechanism, there has been a concerted effort to identify PTC therapeutics. Most clinical trials for PTC therapeutics have been conducted with small molecules that promote PTC read through and incorporation of a near-cognate amino acid. However, there is a need for PTC suppression agents that recode PTCs with the correct amino acid while being applicable to PTC mutations in many different genomic landscapes. With these characteristics, a single therapeutic will be able to treat several disease-causing PTCs. In this review, we will focus on the use of nonsense suppression technologies, in particular, suppressor tRNAs (sup-tRNAs), as possible therapeutics for correcting PTCs. Sup-tRNAs have many attractive qualities as possible therapeutic agents although there are knowledge gaps on their function in mammalian cells and technical hurdles that need to be overcome before their promise is realized. This article is categorized under: RNA Processing > tRNA Processing Translation > Translation Regulation.
Keywords: gene expression; nonsense mutation; nonsense suppression therapy; nonsense suppressor tRNA; premature termination codon mutations; readthrough; translation.
© 2021 The Authors. WIREs RNA published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared no conflicts of interest for this article.
Figures

References
-
- Anderson, J. C. , Wu, N. , Santoro, S. W. , Lakshman, V. , King, D. S. , & Schultz, P. G. (2004). An expanded genetic code with a functional quadruplet codon. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 101(20), 7566–7571. 10.1073/pnas.0401517101 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ashton, L. J. , Brooks, D. A. , McCourt, P. A. , Muller, V. J. , Clements, P. R. , & Hopwood, J. J. (1992). Immunoquantification and enzyme kinetics of alpha‐L‐iduronidase in cultured fibroblasts from normal controls and mucopolysaccharidosis type I patients. American Journal of Human Genetics, 50(4), 787–794. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

