The Application of Nanobody in CAR-T Therapy
- PMID: 33567640
- PMCID: PMC7914546
- DOI: 10.3390/biom11020238
The Application of Nanobody in CAR-T Therapy
Abstract
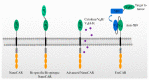
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T therapy represents a form of immune cellular therapy with clinical efficacy and a specific target. A typical chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) construct consists of an antigen binding domain, a transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic domain. Nanobodies have been widely applied as the antigen binding domain of CAR-T due to their small size, optimal stability, high affinity, and manufacturing feasibility. The nanobody-based CAR structure has shown a proven function in more than ten different tumor-specific targets. After being transduced in Jurkat cells, natural killer cells, or primary T cells, the resulting nanobody-based CAR-T or CAR-NK cells demonstrate anti-tumor effects both in vitro and in vivo. Interestingly, anti-BCMA CAR-T modulated by a single nanobody or bi-valent nanobody displays comparable clinical effects with that of single-chain variable fragment (scFv)-modulated CAR-T. The application of nanobodies in CAR-T therapy has been well demonstrated from bench to bedside and displays great potential in forming advanced CAR-T for more challenging tasks.
Keywords: BCMA; CAR-T; VHH; nanobody.
Conflict of interest statement
Chaolemeng Bao, Bingxiang Zhang, Yijin Ding, Zongpei Song, Ruining Zhang, Jishuai Zhang, and Xian-Hui Wu have received supports from Shenzhen Pregene Biopharma Co., Ltd. All the other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Bouchkouj N., Kasamon Y.L., de Claro R.A., George B., Lin X., Lee S., Blumenthal G.M., Bryan W., McKee A.E., Pazdur R. FDA Approval Summary: Axicabtagene Ciloleucel for Relapsed or Refractory Large B-cell Lymphoma. Clin. Cancer Res. 2019;25:1702–1708. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-18-2743. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

