Suppression of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1α by Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin Mitigates Ventilation-Induced Diaphragm Dysfunction in a Murine Endotoxemia Model
- PMID: 33567713
- PMCID: PMC7914863
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms22041702
Suppression of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1α by Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin Mitigates Ventilation-Induced Diaphragm Dysfunction in a Murine Endotoxemia Model
Abstract
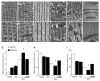
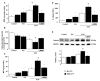
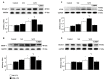
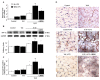
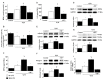
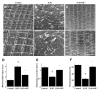
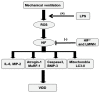
Mechanical ventilation (MV) is required to maintain life for patients with sepsis-related acute lung injury but can cause diaphragmatic myotrauma with muscle damage and weakness, known as ventilator-induced diaphragm dysfunction (VIDD). Hypoxia-inducible factor 1α (HIF-1α) plays a crucial role in inducing inflammation and apoptosis. Low-molecular-weight heparin (LMWH) was proven to have anti-inflammatory properties. However, HIF-1α and LMWH affect sepsis-related diaphragm injury has not been investigated. We hypothesized that LMWH would reduce endotoxin-augmented VIDD through HIF-1α. C57BL/6 mice, either wild-type or HIF-1α-deficient, were exposed to MV with or without endotoxemia for 8 h. Enoxaparin (4 mg/kg) was administered subcutaneously 30 min before MV. MV with endotoxemia aggravated VIDD, as demonstrated by increased interleukin-6 and macrophage inflammatory protein-2 levels, oxidative loads, and the expression of HIF-1α, calpain, caspase-3, atrogin-1, muscle ring finger-1, and microtubule-associated protein light chain 3-II. Disorganized myofibrils, disrupted mitochondria, increased numbers of autophagic and apoptotic mediators, substantial apoptosis of diaphragm muscle fibers, and decreased diaphragm function were also observed (p < 0.05). Endotoxin-exacerbated VIDD and myonuclear apoptosis were attenuated by pharmacologic inhibition by LMWH and in HIF-1α-deficient mice (p < 0.05). Our data indicate that enoxaparin reduces endotoxin-augmented MV-induced diaphragmatic injury, partially through HIF-1α pathway inhibition.
Keywords: endotoxemia; hypoxia-inducible factor-1α; low-molecular-weight heparin; mitochondria; ventilator-induced diaphragm dysfunction.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors have read the journal’s policy on disclosure of potential conflicts of interest and declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Reduction in Ventilation-Induced Diaphragmatic Mitochondrial Injury through Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1α in a Murine Endotoxemia Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 19;23(3):1083. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031083. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163007 Free PMC article.
-
Low-Molecular-Weight Heparin Reduces Ventilation-Induced Lung Injury through Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1α in a Murine Endotoxemia Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Apr 28;21(9):3097. doi: 10.3390/ijms21093097. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 32353952 Free PMC article.
-
Attenuation of ventilation-induced diaphragm dysfunction through toll-like receptor 4 and nuclear factor-κB in a murine endotoxemia model.Lab Invest. 2018 Sep;98(9):1170-1183. doi: 10.1038/s41374-018-0081-0. Epub 2018 Jun 20. Lab Invest. 2018. PMID: 29925937
-
Ventilator-induced diaphragm dysfunction in critical illness.Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2018 Dec;243(17-18):1329-1337. doi: 10.1177/1535370218811950. Epub 2018 Nov 19. Exp Biol Med (Maywood). 2018. PMID: 30453774 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ventilator-induced diaphragm dysfunction: cause and effect.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2013 Sep;305(5):R464-77. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00231.2013. Epub 2013 Jul 10. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2013. PMID: 23842681 Review.
Cited by
-
Heparin and Heparin-Based Drug Delivery Systems: Pleiotropic Molecular Effects at Multiple Drug Resistance of Osteosarcoma and Immune Cells.Pharmaceutics. 2022 Oct 13;14(10):2181. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics14102181. Pharmaceutics. 2022. PMID: 36297616 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α is a biomarker for predicting patients with sepsis.J Int Med Res. 2023 Sep;51(9):3000605231202139. doi: 10.1177/03000605231202139. J Int Med Res. 2023. PMID: 37773726 Free PMC article.
-
Prolonged Mechanical Ventilation: Outcomes and Management.J Clin Med. 2022 Apr 27;11(9):2451. doi: 10.3390/jcm11092451. J Clin Med. 2022. PMID: 35566577 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of ferroptosis-associated genes and potential pharmacological targets in sepsis-induced myopathy.Heliyon. 2024 Mar 30;10(7):e29062. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e29062. eCollection 2024 Apr 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38601693 Free PMC article.
-
Reduction in Ventilation-Induced Diaphragmatic Mitochondrial Injury through Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1α in a Murine Endotoxemia Model.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 19;23(3):1083. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031083. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163007 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maes K., Stamiris A., Thomas D., Cielen N., Smuder A., Powers S.K., Leite F.D.S., Hermans G., Decramer M., Hussain S.N., et al. Effects of Controlled Mechanical Ventilation on Sepsis-Induced Diaphragm Dysfunction in Rats. Crit. Care Med. 2014;42:e772–e782. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000000685. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Picard M., Liang F., Hussain S.N., Goldberg P., Danialou G., Chaturvedi R., Matecki S., Samir J., Rosiers C.D., Karpati G., et al. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Lipid Accumulation in The Human Diaphragm During Mechanical Ventilation. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2012;186:1140–1149. doi: 10.1164/rccm.201206-0982OC. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

