Prognostic values of tumoral MMP2 and MMP9 overexpression in breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
- PMID: 33568081
- PMCID: PMC7877076
- DOI: 10.1186/s12885-021-07860-2
Prognostic values of tumoral MMP2 and MMP9 overexpression in breast cancer: a systematic review and meta-analysis
Abstract
Background: Breast cancer (BC) is a leading cause of cancer-related death in females worldwide. Previous studies have demonstrated that matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) play key roles in metastasis and are associated with survival in various cancers. The prognostic values of MMP2 and MMP9 expression in BC have been investigated, but the results remain controversial. Thus, we performed the present meta-analysis to investigate the associations between MMP2/9 expressions in tumor cells with clinicopathologic features and survival outcome in BC patients.
Methods: Eligible studies were searched in PubMed, Web of Science, EMBASE, CNKI and Wanfang databases. The associations of MMP2/9 overexpression in tumor cells with overall survival (OS), disease-free survival (DFS) and recurrence-free survival (RFS) were assessed by hazard ratio (HR) and 95% confidence interval (CI). The associations of MMP2/9 overexpression with clinicopathological features were investigated by calculating odds ratio (OR) and 95% CI. Subgroup analysis, sensitivity analysis, meta-regression, and analysis for publication bias were performed.
Results: A total of 41 studies comprising 6517 patients with primary BC were finally included. MMP2 overexpression was associated with an unfavorable OS (HR = 1.60, 95% CI 1.33 -1.94, P < 0.001) while MMP9 overexpression predicted a shorter OS (HR = 1.52, 95% CI 1.30 -1.77, P < 0.001). MMP2 overexpression conferred a higher risk to distant metastasis (OR = 2.69, 95% CI 1.35-5.39, P = 0.005) and MMP9 overexpression correlated with lymph node metastasis (OR = 2.90, 95% CI 1.86 - 4.53, P < 0.001). Moreover, MMP2 and MMP9 overexpression were both associated with higher clinical stage and histological grade in BC patients. MMP9 overexpression was more frequent in patients with larger tumor sizes.
Conclusions: Tumoral MMP2 and MMP9 are promising markers for predicting the prognosis in patients with BC.
Keywords: Breast cancer; MMP2; MMP9; Meta-analysis; Survival.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
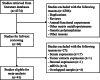
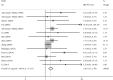
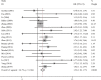
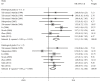
Similar articles
-
Relationship between matrix metalloproteinase 2 and lung cancer progression.Mol Diagn Ther. 2007;11(3):183-92. doi: 10.1007/BF03256240. Mol Diagn Ther. 2007. PMID: 17570740
-
Prognostic value of matrix metalloproteinase 9 expression in breast cancer patients: a meta-analysis.Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013;14(3):1615-21. doi: 10.7314/apjcp.2013.14.3.1615. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 2013. PMID: 23679245
-
Matrix metalloproteinases MMP1, MMP2, MMP9 and their tissue inhibitors TIMP1, TIMP2, TIMP3 in head and neck cancer: an immunohistochemical study.Otolaryngol Pol. 2016 Jun 30;70(3):32-43. doi: 10.5604/00306657.1202546. Otolaryngol Pol. 2016. PMID: 27386931
-
Association of MMP2 and MMP9 gene polymorphisms with the recurrent spontaneous abortion: A meta-analysis.Gene. 2021 Jan 30;767:145173. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2020.145173. Epub 2020 Sep 29. Gene. 2021. PMID: 33007375 Review.
-
Relationships between abnormal MMP2 expression and prognosis in gastric cancer: a meta-analysis of cohort studies.Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2014 May;29(4):166-72. doi: 10.1089/cbr.2014.1608. Epub 2014 Apr 30. Cancer Biother Radiopharm. 2014. PMID: 24784911 Review.
Cited by
-
The Proapoptotic Action of Pyrrolidinedione-Thiazolidinone Hybrids towards Human Breast Carcinoma Cells Does Not Depend on Their Genotype.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Aug 22;16(16):2924. doi: 10.3390/cancers16162924. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39199694 Free PMC article.
-
Immunomodulatory role of metalloproteases in cancers: Current progress and future trends.Front Immunol. 2022 Dec 16;13:1064033. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.1064033. eCollection 2022. Front Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36591235 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Silencing of integrin subunit α3 inhibits the proliferation, invasion, migration and autophagy of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma cells.Oncol Lett. 2022 Jun 20;24(2):271. doi: 10.3892/ol.2022.13391. eCollection 2022 Aug. Oncol Lett. 2022. PMID: 35782901 Free PMC article.
-
A Bioinformatics Assessment Indicating Better Outcomes With Breast Cancer Resident, Immunoglobulin CDR3-MMP2 Binding.Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2023 May-Jun;20(3):239-246. doi: 10.21873/cgp.20378. Cancer Genomics Proteomics. 2023. PMID: 37093687 Free PMC article.
-
Aged Breast Extracellular Matrix Drives Mammary Epithelial Cells to an Invasive and Cancer-Like Phenotype.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021 Nov;8(22):e2100128. doi: 10.1002/advs.202100128. Epub 2021 Oct 7. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2021. PMID: 34617419 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Parise CA, Bauer KR, Brown MM, Caggiano V. Breast cancer subtypes as defined by the estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PR), and the human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2) among women with invasive breast cancer in California, 1999-2004. Breast J. 2009;15(6):593–602. doi: 10.1111/j.1524-4741.2009.00822.x. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

