Breastfeeding practice in China from 2013 to 2018: a study from a national dynamic follow-up surveillance
- PMID: 33568130
- PMCID: PMC7874457
- DOI: 10.1186/s12889-021-10211-2
Breastfeeding practice in China from 2013 to 2018: a study from a national dynamic follow-up surveillance
Abstract
Background: Breastfeeding is important for the physical and psychological health of the mother and child. Basic data on breastfeeding practice in China are out-of-date and vary widely. This study aimed to evaluate the progress of breastfeeding practice in China, as well as to explore the bottlenecks in driving better practice.
Methods: This was an observational study. We used data from the Under-5 Child Nutrition and Health Surveillance System in China for the period 2013-2018. The prevalence of early initiation of breastfeeding (EIBF) and exclusive breastfeeding (EBF) were calculated for each year for subgroups of China. The Cochran-Armitage test was used to explore the time trends. The annual percent of change (APC) were calculated by log-linear regression followed by exp transformation.
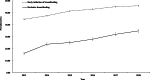
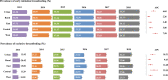
Results: The prevalence of EIBF increased significantly from 44.57% (95% CI: 44.07, 45.07) in 2013 to 55.84% (95% CI: 55.29, 56.38) in 2018 (Ptrend < 0.001), with an APC of 4.67% (95% CI: 3.51, 5.85). And the prevalence of EBF increased rapidly from 16.14% (95% CI: 15.10, 17.18) to 34.90% (95% CI: 33.54, 36.26) (Ptrend < 0.001), with an APC of 14.90% (95% CI: 9.97, 20.04). Increases were observed in both urban and rural areas, with urban areas showing greater APCs for EIBF (6.05%; 95% CI: 4.22, 7.92 v.s. 2.26%; 95% CI: 1.40, 3.12) and EBF (18.21%; 95% CI: 11.53, 25.29 v.s. 9.43%; 95% CI: 5.52, 13.49). The highest EBF prevalence was observed in the East, but the Central area showed the highest APC. The prevalence of EBF decreased with increasing age within the first 6 months, especially after 3 months.
Conclusion: The prevalence of both EIBF and EBF in China are improving in recent years. The rural and West China could be the key areas in the future actions. More efforts should be made to protect and promote breastfeeding to achieve near- and long-term goals for child health.
Keywords: Dynamic surveillance; Early initiation of breastfeeding; Exclusive breastfeeding; Geographic disparities; Trend.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Horta BL, Victora CG. Short-term effects of breastfeeding: a systematic review on the benefits of breastfeeding on diarrhoea and pneumonia mortality. Geneva: World Health Organization; 2013.
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

