Roxadustat for Treating Anemia in Patients with CKD Not on Dialysis: Results from a Randomized Phase 3 Study
- PMID: 33568383
- PMCID: PMC7920165
- DOI: 10.1681/ASN.2020081150
Roxadustat for Treating Anemia in Patients with CKD Not on Dialysis: Results from a Randomized Phase 3 Study
Abstract
Background: Current anemia therapies for patients with non-dialysis-dependent CKD may require injection and medical visits. Roxadustat, an oral hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor, stimulates erythropoiesis and improves iron homeostasis.
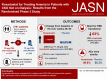
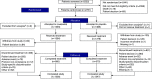
Methods: In this double-blind phase 3 study, we randomized patients with non-dialysis-dependent CKD stages 3-5 and hemoglobin <10.0 g/dl (1:1) to thrice-weekly 70-mg oral roxadustat or placebo. Doses were titrated throughout the study based on hemoglobin levels. The primary efficacy end point was mean change from baseline in hemoglobin averaged over weeks 28-52 versus placebo, irrespective of rescue therapy use. We assessed patients for adverse events.
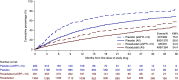
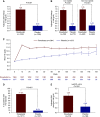
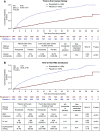
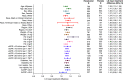
Results: The study included 2781 patients, 1393 who received roxadustat and 1388 who received placebo. Mean baseline hemoglobin was 9.1 g/dl for both groups. The mean change in hemoglobin from baseline was 1.75 g/dl (95% confidence interval [95% CI], 1.68 to 1.81) with roxadustat versus 0.40 g/dl (95% CI, 0.33 to 0.47) with placebo, (P<0.001). Among 411 patients with baseline elevated high-sensitivity C-reactive protein, mean change in hemoglobin from baseline was 1.75 g/dl (95% CI, 1.58 to 1.92) with roxadustat versus 0.62 g/dl (95% CI, 0.44 to 0.80) with placebo, (P<0.001). Roxadustat reduced the risk of red blood cell transfusion by 63% (hazard ratio, 0.37; 95% CI, 0.30 to 0.44). The most common adverse events with roxadustat and placebo, respectively, were ESKD (21.0% versus 20.5%), urinary tract infection (12.8% versus 8.0%), pneumonia (11.9% versus 9.4%), and hypertension (11.5% versus 9.1%).
Conclusions: Roxadustat effectively increased hemoglobin in patients with non-dialysis-dependent CKD and reduced the need for red blood cell transfusion, with an adverse event profile comparable to that of placebo.
Clinical trial registry name and registration number: Safety and Efficacy Study of Roxadustat to Treat Anemia in Patients With CKD, Not on Dialysis, NCT02174627.
Keywords: anemia; chronic kidney disease; clinical nephrology; clinical trial; randomized controlled trials.
Copyright © 2021 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Figures


Comment in
-
Authors' Reply.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021 Jun 1;32(6):1537-1538. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2021030334. Epub 2021 Apr 13. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 33849916 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
On the Increased Event Rate of Urinary Tract Infection and Pneumonia in CKD Patients Treated with Roxadustat for Anemia.J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021 Jun 1;32(6):1537. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2021020204. Epub 2021 Apr 13. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2021. PMID: 33849917 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- McClellan W, Aronoff SL, Bolton WK, Hood S, Lorber DL, Tang KL, et al. .: The prevalence of anemia in patients with chronic kidney disease. Curr Med Res Opin 20: 1501–1510, 2004 - PubMed
-
- Jungers PY, Robino C, Choukroun G, Nguyen-Khoa T, Massy ZA, Jungers P: Incidence of anaemia, and use of epoetin therapy in pre-dialysis patients: A prospective study in 403 patients. Nephrol Dial Transplant 17: 1621–1627, 2002 - PubMed
-
- Wong MMY, Tu C, Li Y, Perlman RL, Pecoits-Filho R, Lopes AA, et al. .; CKDopps Investigators: Anemia and iron deficiency among chronic kidney disease Stages 3-5ND patients in the Chronic Kidney Disease Outcomes and Practice Patterns Study: Often unmeasured, variably treated. Clin Kidney J 13: 613–624, 2019 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Cases-Amenós A, Martínez-Castelao A, Fort-Ros J, Bonal-Bastons J, Ruiz MP, Vallés-Prats M, et al. .: Prevalence of anaemia and its clinical management in patients with stages 3-5 chronic kidney disease not on dialysis in Catalonia: MICENAS I study. Nefrologia 34: 189–198, 2014 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

