Lower Plasma Melatonin in the Intervertebral Disk Degeneration Patients Was Associated with Increased Proinflammatory Cytokines
- PMID: 33568902
- PMCID: PMC7869702
- DOI: 10.2147/CIA.S290045
Lower Plasma Melatonin in the Intervertebral Disk Degeneration Patients Was Associated with Increased Proinflammatory Cytokines
Abstract
Background: Intervertebral disc degeneration (IDD) was considered to be the pathological basis of intervertebral disc herniation (IDH). However, the plasma melatonin in the IDD cases and healthy controls remained unclear.
Methods: In this case-control study, a total of 71 IDD cases and 54 healthy controls were enrolled between April 2020 and August 2020. The diagnostic effect of plasma melatonin for IDD was detected using receiver operating characteristic curve. The correlations between two continuous variables were detected with the Pearson linear analyses.
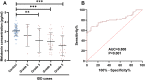
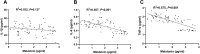
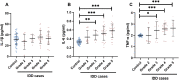
Results: It was found that lower melatonin concentration was detected in the IDD cases (1.906 ± 1.041 vs 3.072 ± 0.511 pg/mL, P<0.001). Through receiver operating characteristic curve analyses, it was found that plasma melatonin could be used as a diagnostic biomarker for IDD (area under curve=0.808, P<0.001). In advanced correlation analyses, it was found that plasma melatonin concentration was negatively associated with the age, symptom durations, IDD disease severity and proinflammatory factors, including IL-6 and TNF-α concentrations (P<0.05). Comparing with the higher melatonin groups, significantly increased IL-6 (0.601 ± 0.085 vs 0.507 ± 0.167 pg/mL, P=0.028) and TNF-α (3.022 ± 0.286 vs 2.353 ± 0.641, P<0.001) were detected in the patients with lower melatonin concentration.
Conclusion: The plasma melatonin concentration was significantly decreased in the IDD cases and plasma melatonin could be used as a diagnostic biomarker for IDD. Lower plasma melatonin was associated with longer disease durations, elevated disease severity and higher inflammatory cytokines levels in IDD patients.
Keywords: biomarker; inflammatory factors; intervertebral disc degeneration; melatonin.
© 2021 Tian et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

References
-
- Li Y, Ma J, Yao K, et al. Circadian rhythms and obesity: timekeeping governs lipid metabolism. J Pineal Res. 2020;e12682. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

